Asus ITX-220: 6 DHCPServerConguration
6 DHCPServerConguration: Asus ITX-220

iPBX30 User Manual
Chapter 6
6 DHCPServerConguration
6.1 Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP)
6.1.1 What is DHCP?
DHCP is a protocol that enables network administrators to centrally
manage the assignment and distribution of IP information to
computers on a network.
When you enable DHCP on a network, you allow a device —
such as the iPBX30 — to assign temporary IP addresses to your
computers whenever they connect to your network. The assigning
device is called a DHCP server, and the receiving device is a DHCP
client.
Note: If you followed the instructions in chapter 3, you
either configured each LAN PC with an IP address,
or you specified that it will receive IP information
dynamically (automatically). If you chose to have the
information assigned dynamically, then you congured
your PCs as DHCP clients that will accept IP addresses
assigned from a DCHP server such as the
iPBX30
.
The DHCP server draws from a dened pool of IP addresses and
“leases” them for a specified amount of time to your computers
when they request an Internet session. It monitors, collects, and
redistributes the addresses as needed.
On a DHCP-enabled network, the IP information is assigned
dynamically rather than statically. A DHCP client can be assigned
a different address from the pool each time it reconnects to the
network.
6.1.2 Why use DHCP?
DHCP allows you to manage and distribute IP addresses throughout
your network from the iPBX30. Without DHCP, you would have to
configure each computer separately with IP address and related
information. DHCP is commonly used with large networks and
those that are frequently expanded or otherwise updated.
45
Chapter 6
iPBX30 User Manual
6.1.3 ConguringDHCPServer
Note: By default, the iPBX30 is configured as a
DHCP server on the LAN side, with a predened IP
address pool of 192.168.1.100 through 192.168.1.149
(subnet mask 255.255.255.0). To change this range
of addresses, follow the procedures described in this
section.
First, you must configure your PCs to accept DHCP information
assigned by a DHCP server:
1. Click
Advanced -> DHCP Server
menu to open the DHCP
Server Conguration page.
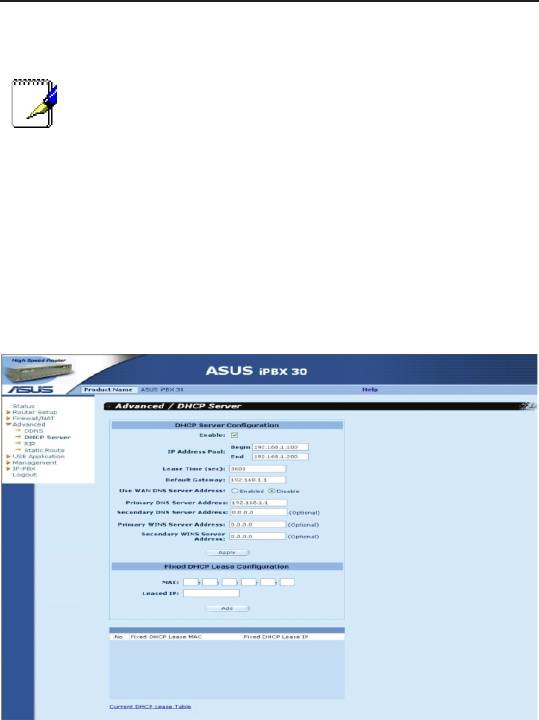
Figure 6.1. DHCP Server Conguration Page
2. Enter the information for the IP Address Pool (Begin/End
Address), Subnet Mask, Lease Time and Default Gateway IP
Address, elds; others, such as Primary/Secondary DNS Server
IP Address and Primary/Secondary WINS Server IP Address
are optional. However, it is recommended that you enter the
primary DNS server IP address in the space provided. You
may enter the LAN IP or your ISP’s DNS IP in the primary DNS
Server IP Address eld. The table below describes the DHCP
conguration parameters in detail.
46

iPBX30 User Manual
Chapter 6
Table 6.1. DHCP Conguration Parameters
Field Description
Enable Check or uncheck this box to enable or disable the DHCP
server service for your LAN.
IP Address
Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the DHCP
address pool.
Pool Begin/End
Lease Time The amount of time in seconds the assigned address will
be used by a device connected on the LAN.
Default
The address of the default gateway for computers that
receive IP addresses from this pool. The default gateway
Gateway IP
is the device that the DHCP client computers first
Address
contacted to communicate with the Internet. Typically, it is
the iPBX30’s LAN port IP address.
Primary/
The IP address of the Domain Name System server to be
used by computers that receive IP addresses from this
Secondary
pool. The DNS server translates common Internet names
DNS Server IP
that you type into your web browser into their equivalent
Address
numeric IP addresses. Typically, the server(s) are located
with your ISP. However, you may enter LAN IP address
of the iPBX30 as it will serve as DNS proxy for the LAN
computers and forward the DNS request from the LAN
to DNS servers and relay the results back to the LAN
computers. Note that both the primary and secondary
DNS servers are optional.
Primary/
The IP address of the WINS servers to be used by
computers that receive IP addresses from the DHCP IP
Secondary
address pool. You don’t need to enter this information
WINS Server
unless your network has WINS servers.
IP Address
(optional)
3. Click
Apply
to save the DHCP server congurations.
47
Chapter 6
iPBX30 User Manual
6.1.4 Viewing Current DHCP Address Assignments
When the iPBX30 functions as a DHCP server for your LAN, it
keeps a record of any addresses it has leased to your computers.
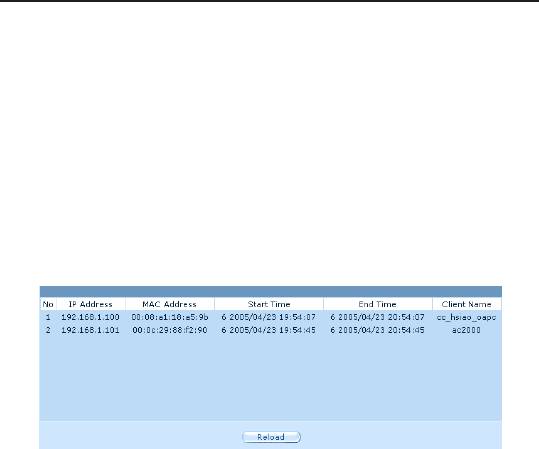
To view a table of all current IP address assignments, just open
the DHCP Server Conguration page and click on the link “Current
DHCP Lease Table” located at the bottom of the conguration page.
The DHCP lease table lists any IP addresses leased and the
corresponding MAC addresses.
Figure 6.2. DHCP Lease Table
6.1.5 Fixed DHCP Lease
Fixed DHCP lease is used in situations when a xed DHCP address
is desired for a host that gets IP from the DHCP server. First, you
should congure your PCs to accept DHCP information assigned
by a DHCP server:
6.1.5.1
AccessFixedDHCPCongurationPage–(Advanced
->DHCP Server)
Click
Advanced ->DHCP Server
menu to open the Fixed DHCP
Lease conguration page.
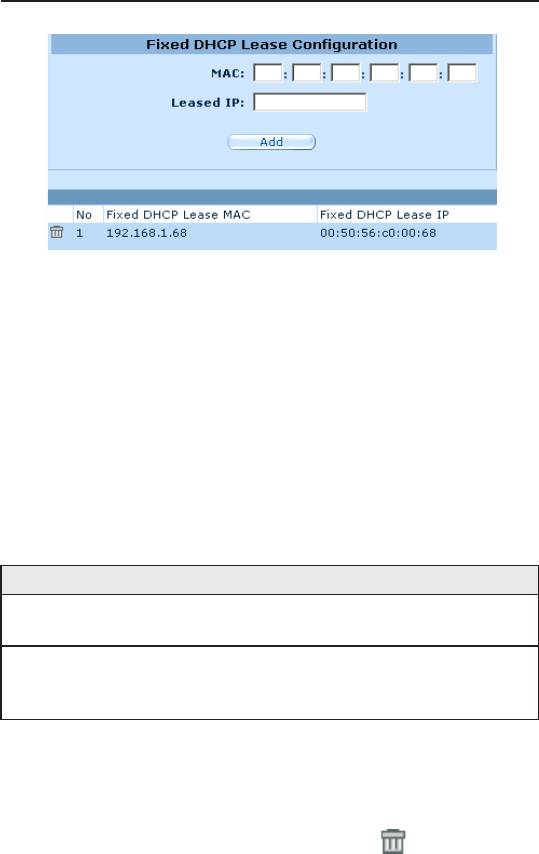
When you open the Fixed DHCP Lease configuration page, a
list of existing lease is also displayed at the bottom half of the
conguration page.
48
iPBX30 User Manual
Chapter 6
Figure 6.3. Fixed DHCP Lease Conguration Page
6.1.5.2 Add a Fixed DHCP Lease
To add a xed DHCP lease, follow the instructions below:
1. Click
Advanced ->DHCP Server
menu to open the Fixed DHCP
Lease conguration page.
2. Enter the MAC address and the desired IP address of the host
requiring a xed IP address. The table below describes the xed
DHCP lease conguration parameters in detail.
Table 6.2. Fixed DHCP Lease Conguration Parameters
Field Description
Fixed DHCP Lease
A hardware ID of the device that needs a fixed IP
MAC
address from the DHCP server.
Fixed DHCP Lease IP The IP address leased from the DHCP server. It is
recommended that this IP address be outside of the
DHCP IP pool.
3. Click on the
Add
button to add the new xed DHCP lease entry.
6.1.5.3 Delete a Fixed DHCP Lease
To delete a fixed DHCP lease, click on the in front of the
specic xed DHCP lease to be deleted.
6.1.5.4 Viewing Fixed DHCP Lease Table
To see existing inbound fixed DHCP lease, just open the Fixed
DHCP Lease configuration page by clicking
Advanced ->DHCP
Server
menu.
49

Chapter 6
iPBX30 User Manual
6.2 DNS
6.2.1 About DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) servers map the user-friendly domain
names that users type into their Web browsers (e.g., “yahoo.com”)
to the equivalent numerical IP addresses that are used for Internet
routing.
When a PC user types a domain name into a browser, the PC must
first send a request to a DNS server to obtain the equivalent IP
address. The DNS server will attempt to look up the domain name
in its own database, and will communicate with higher-level DNS
servers when the name cannot be found locally. When the address
is found, it is sent back to the requesting PC and is referenced in IP
packets for the remainder of the communication.
6.2.2 Assigning DNS Addresses
Multiple DNS addresses are useful to provide alternatives when
one of the servers is down or is encountering heavy traffic. ISPs
typically provide primary and secondary DNS addresses, and may
provide additional addresses. Your LAN PCs learn these DNS
addresses in one of the following ways:
• Statically: If your ISP provides you with their DNS server
addresses, you can assign them to each PC by modifying the
PCs’ IP properties.
• Dynamically from a DHCP Server: You can congure the DNS
addresses in the DHCP server in the iPBX30 and allow the
DHCP server to distribute the DNS addresses to the PCs. Refer
to the section 6.1.3 “Conguring DHCP Server” for instructions
on conguring DHCP server.
In either case, you can specify the actual addresses of the ISP’s
DNS servers (on the PC or in the DHCP Server conguration page),
or you can specify the address of the LAN port on the iPBX30
(e.g., 192.168.1.1). When you specify the LAN port IP address, the
device performs DNS relay, as described in the following section.
Note: If you specify the actual DNS addresses on the
PCs or in the DHCP pool, the DNS relay feature is not
used.
50

iPBX30 User Manual
Chapter 6
6.2.3 ConguringDNSRelay
When you specify the device’s LAN port IP address as the DNS
address, then the Internet Security Router automatically performs
“DNS relay”; i.e., because the device itself is not a DNS server, it
forwards domain name lookup requests from the LAN PCs to a
DNS server at the ISP. It then relays the DNS server’s response to
the PC.
When performing DNS relay, the iPBX30 must maintain the IP
addresses of the DNS servers it contacts. It can learn these
addresses in either or both of the following ways:
• Learned through PPPoE or Dynamic IP Connection: If the
iPBX30 uses a PPPoE (see section 5.2.2 PPPoE or 5.2.3
PPPoE or Dynamic IP (see section 5.2.4 Dynamic IP)
connection to the ISP, the primary and secondary DNS
addresses can be learned via the PPPoE protocol. Using
this option provides the advantage that you will not need to
recongure the PCs or the iPBX30 if the ISP changes their DNS
addresses.
• Congured on the iPBX30: You can also specify the ISP’s DNS
addresses in the WAN conguration page.
Follow these steps to congure DNS relay:
1. Enter LAN IP in the DNS Server IP Address field in DHCP
conguration page.
2. Configure the LAN PCs to use the IP addresses assigned by
the DHCP server on the Internet Security Router, or enter the
Internet Security Router’s LAN IP address as their DNS server
address manually for each PC on your LAN.
Note: DNS addresses that are assigned to LAN PCs
prior to enabling DNS relay will remain in effect until
the PC is rebooted. DNS relay will only take effect
when a PC’s DNS address is the LAN IP address.
Similarly, if after enabling DNS relay, you specify a
DNS address (other than the LAN IP address) in a
DHCP pool or statically on a PC, then that address
will be used instead of the DNS relay address.
51
Оглавление
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Getting to Know your iPBX30
- 3 Quick Start Guide
- 4 Using the Web UI Management
- 5 Router Setup
- 6 DHCPServerConguration
- 7 Routing
- 8 ConguringDDNS
- 9 ConguringFirewallandNAT
- 10 USB Application
- 11 System Management
- 12 SIP IP-PBX
- 13 IP Addresses, Network Masks, and Subnets
- 14 Troubleshooting
- 15 Index

