Gigabyte GA-MA78LMT-S2H: Chapter 5 Appendix
Chapter 5 Appendix: Gigabyte GA-MA78LMT-S2H

Chapter 5 Appendix
5-1 Conguring SATA Hard Drive(s)
To congure SATA hard drive(s), follow the steps below:
A. Install SATA hard drive(s) in your computer.
B. Congure SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup.
(Note 1)
C. Congure a RAID array in RAID BIOS.
(Note 2)
D. Make a oppy disk containing the SATA RAID/AHCI driver for Windows XP.
(Note 2)
E. Install the SATA RAID/AHCI driver
and operating system.
Before you begin
Please prepare:
• At least two SATA hard drives (to ensure optimal performance, it is recommended that you use two hard
drives with identical model and capacity). If you do not want to create RAID, you may prepare only one
hard drive.
• An empty formatted oppy disk.
• Windows Vista/XP setup disk.
• Motherboard driver disk.
5-1-1 Conguring the Onboard SATA Controller
A. Installing SATA hard drive(s) in your computer
Attach one end of the SATA signal cable to the rear of the SATA hard drive and the other end to available
SATA port on the motherboard. Then connect the power connector from your power supply to the hard drive.
(Note 1) Skip this step if you do not want to create RAID array on the SATA controller.
(Note 2) Required when the SATA controller is set to AHCI or RAID mode.
- 77 - Appendix

B. Conguring SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup
Make sure to congure the SATA controller mode correctly in system BIOS Setup.
Step 1:
Turn on your computer and press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup during the POST (Power-On Self-Test).
Ensure OnChip SATA Controller is enabled under Integrated Peripherals. To enable RAID for the
SATA2_0/1/2/3 connectors, set OnChip SATA Type to RAID. To enable RAID for the SATA2_4/ESATA con-
nectors, set OnChip SATA Type to RAID and set OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type to As SATA Type (Figure 1).
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2009 Award Software
Integrated Peripherals
OnChip IDE Channel [Enabled]
Item Help
OnChip SATA Controller [Enabled]
Menu Level
OnChip SATA Type [RAID]
OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type [As SATA Type]
Onboard LAN Function [Enabled]
Onboard LAN Boot ROM [Disabled]
SMART LAN [Press Enter]
Onboard Audio Function [Enabled]
OnChip USB Controller [Enabled]
USB EHCI Controller [Enabled]
USB Keyboard Support [Enabled]
USB Mouse Support [Disabled]
Legacy USB storage detect [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8/IRQ4]
Onboard Parallel Port [378/IRQ7]
Parallel Port Mode [SPP]
x ECP Mode Use DMA 3
higf
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Figure 1
Step 2:
Save changes and exit BIOS Setup.
The BIOS Setup menus described in this section may differ from the exact settings for your moth-
erboard. The actual BIOS Setup menu options you will see shall depend on the motherboard you
have and the BIOS version.
Appendix - 78 -

C. Conguring RAID set in RAID BIOS
Enter the RAID BIOS setup utility to congure a RAID array. Skip this step and proceed with the installation of
Windows operating system for a non-RAID conguration.
Step 1:
After the POST memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins, look for a message which
says "Press <Ctrl-F> to enter FastBuild (tm) Utility" (Figure 2). Press <Ctrl> + <F> to enter the RAID BIOS
setup utility.
RAID Option ROM Version 3.0.1540.33
(c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
NoArrayisdened..
Press <Ctrl-F> to enter FastBuild (tm) Utility...
Figure 2
Step 2:
Main Menu
This is the rst option screen when you enter the BIOS RAID Setup utility. (Figure 3).
To view the disk drives assigned to arrays, press <1> to enter the View Drive Assignments window.
To create an array, press <2> to enter the Dene LD window.
To delete an array, press <3> to enter the Delete LD window.
To view controller settings, press <4> to enter the Controller Conguration window.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ Main Menu ]
View Drive Assignments........................... [ 1 ]
DeneLD..................................................[2]
Delete LD.................................................. [ 3 ]
ControllerConguration............................[4]
[ Keys Available ]
Press 1..4 to Select Option [ESC] Exit
Figure 3
- 79 - Appendix

Create Arrays Manually
To create a new array, press <2> to enter the Dene LD Menu window (Figure 4). The Dene LD selection
from the Main Menu allows users to begin the process of manually dening the drive elements and RAID
levels for one or multiple disk arrays.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[DeneLDMenu]
LD No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity (GB) Status
LD 1 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 2 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 3 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 4 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 5 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 6 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 7 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 8 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 9 ---- ---- ----- ----
LD 10 ---- ---- ----- ----
[ Keys Available ]
[
h
] Up [
i
] Down [ESC] Exit [Enter] Select
Figure 4
In Figure 4, use the up or down arrow key to move to a logical disk set and press <Enter> to enter the RAID
conguration menu (Figure 5).
Option ROM Utility (c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[DeneLDMenu]
LD No RAID Mode Total Drv
LD 1 RAID 0 0
Stripe Block: 64 KB Fast Init: ON
Gigabyte Boundary: ON Cache Mode: WriteThru
[ Drives Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB) Assignment
1:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89 N
2:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.02 N
[ Keys Available ]
[ Keys Available ]
[
h
] Up [
i
] Down [ESC] Exit [Space] Change [Ctrl-Y] Save [PgUp/Dn] Page Change
Figure 5
Appendix - 80 -

In the following procedure, we'll create RAID 0 as an example.
1. Under the RAID Mode section, press the <SPACE> key to select RAID 0.
2. Set the Stripe Block size. 64 KB is the default.
3. Under the Drives Assignments section, press the up or down arrow key to highlight a drive.
4. Press the <SPACE> key or <Y>to change the Assignment option to Y. This action adds the drive to the
disk array. The Total Drv section will show the number of disks assigned.
5. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> keys to save the information. The window below will appear.
Fast Initialization option has been selected
It will erase the MBR data of the disk.
<Press Ctrl-Y key if you are sure to erase it>
<Press any other key to ignore this option>
Figure 6
6. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> to clear the MBR or press other keys to ignore this option. Then, the window below
will appear.
Press Ctrl-Y to Modify Array Capacity or press any
other key to use maximum capacity...
Figure 7
7. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> to set the capacity of the RAID array or press other keys to set the array to its maxi-
mum capacity.
8. After the creation is complete, the screen will return to Dene LD Menu where you will see the newly-
created array.
9. Press <Esc> to return to Main Menu and press <Esc> again if you want to exit the RAID BIOS utility.
View Drive Assignments
The View Drive Assignments option in the Main Menu displays whether the attached hard drives are as-
signed to a disk array or are unassigned. Under the Assignment column, drives are labeled with their as-
signed disk array or shown as Free if unassigned.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ View Drives Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB) Assignment
1:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89
Extent 1 79.82 LD 1-1
2:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.2
Extent 1 80.02 LD 1-2
[ Keys Available ]
[
h
] Up [
i
] Down [ESC] Exit [Ctrl+H] Secure Erase [PgUp/Dn] Page Change
Figure 8
- 81 - Appendix
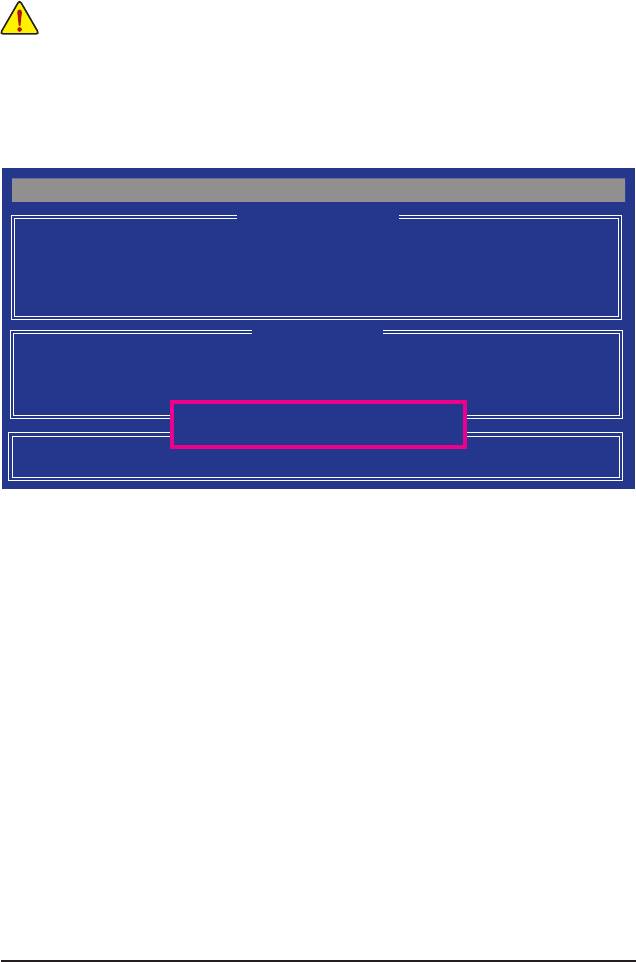
Delete an Array
The Delete Array menu option allows for deletion of disk array assignments.
Deleting an existing disk array could result in loss of data. Record all array information including the
array type, the disk members, and stripe block size in case you wish to undo a deletion.
1. To delete an array, press <3> in the Main Menu to enter the Delete LD Menu. Then highlight the array you
wish to delete and press the <Delete> key or the <Alt>+<D> keys.
2. The View LD Denition Menu will appear (as shown in Figure 9) showing which drives are assigned to
this array. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> if you are sure to delete the array or other keys to abort.
3. When the array is deleted, the screen will return to Delete LD Menu. Press <Esc>to return to Main Menu.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ViewLDDenitionMenu]
LD No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity (GB) Status
LD 1 RAID 0 2 157.99 Functional
Stripe Block: 64KB Cache Mode: WriteThru
[ Drives Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB)
1:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89
2:Mas WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.02
Press Ctrl-Y to delete the data in the disk!
or press any other key to abort...
[ Keys Available ]
[ Keys Available ]
Figure 9
Appendix - 82 -
5-1-2 Making a SATA RAID/AHCI Driver Diskette
(Required for AHCI and RAID Mode)
To successfully install operating system onto SATA hard drive(s) that is/are congured to RAID/AHCI mode,
you need to install the SATA controller driver during the OS installation. Without the driver, the hard drive may
not be recognized during the Windows setup process. First of all, copy the driver for the SATA controller from
the motherboard driver disk to a oppy disk. For installing Windows Vista, you also can copy the SATA con-
troller driver from the motherboard driver disk to a USB ash drive. See the instructions below about how to
copy the driver in MS-DOS and Windows mode.
In MS-DOS mode:
Prepare a startup disk that has CD-ROM support and a blank formatted oppy disk.
Steps:
1: Boot from the startup disk.
2: Remove the startup disk and insert the prepared oppy disk and the motherboard driver disk (here we as-
sume that the drive letter for your optical drive is D:\).
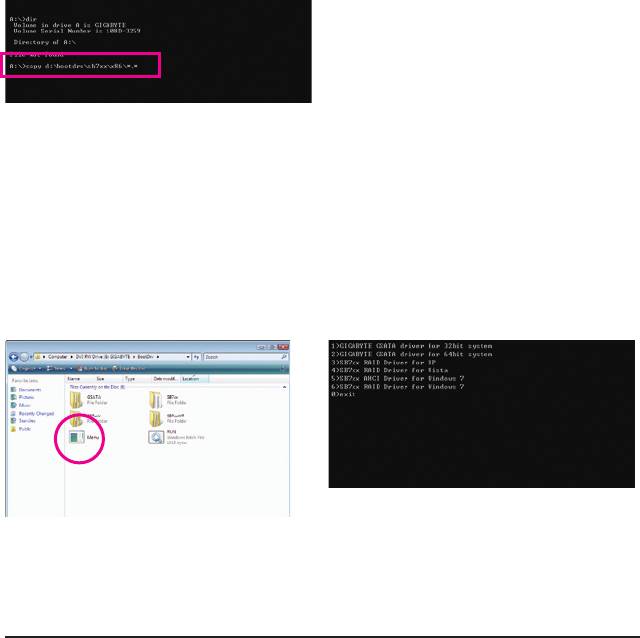
3: At the A:\> prompt, type the following command. Press <Enter> after the command (Figure 1):
(Note)
A:\>copy d:\bootdrv\sb7xx\x86\*.*
Figure 1
In Windows mode:
Steps:
1: Use an alternative system and insert the motherboard driver disk.
2: From your optical drive folder, double click the Menu.exe le in the BootDrv folder (Figure 2). A Command
Prompt window will open similar to that in Figure 3.
3: Insert the blank formatted disk. Select the controller driver by pressing the corresponding letter from the
menu and press <Enter>. For example, from the menu in Figure 3, to install Windows XP to the RAID/
AHCI hard drives, select 3) SB7xx RAID Driver for XP.
Your system will then automatically copy the driver les to the oppy disk. Press any key to exit when nished.
Figure 3
Figure 2
(Note) Change the directory from \x86 to \x64 if you wish to copy the Windows 64-bit driver.
- 83 - Appendix
5-1-3 Installing the SATA RAID/AHCI Driver and Operating System
With the SATA RAID/AHCI driver diskette and correct BIOS settings, you are ready to install Windows Vista/
XP onto your hard drive(s). The followings are examples of Windows XP and Vista installation.
A. Installing Windows XP
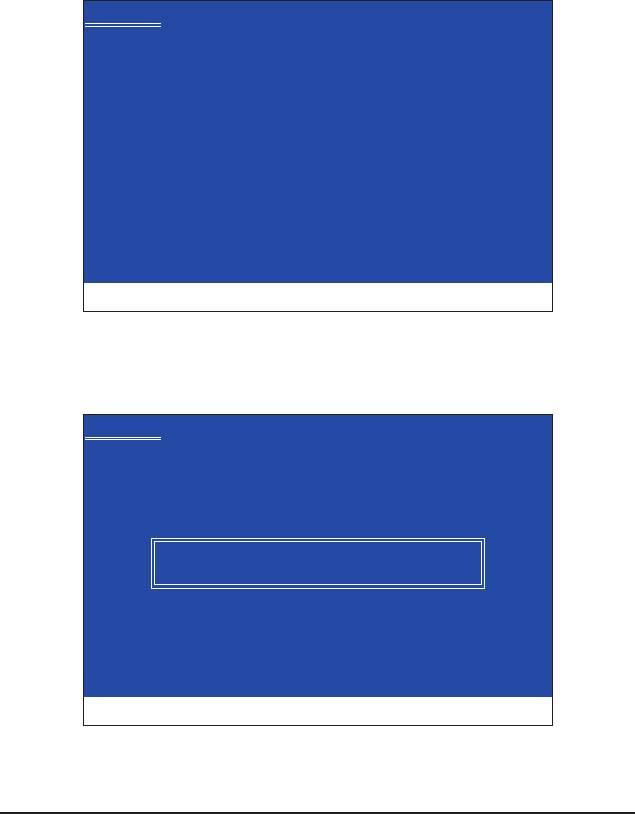
Step 1:
Restart your system to boot from the Windows XP setup disk and press <F6> as soon as you see the mes-
sage "Press F6 if you need to install a 3rd party SCSI or RAID driver" (Figure 1). A screen will then appear
asking you to specify additional device.
Windows Setup
Press F6 if you need to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver.
Figure 1
Step 2:
Insert the oppy disk containing the SATA RAID/AHCI driver and press <S>. Then a controller menu similar
to Figure 2 below will appear. Select AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x86 platform and press
<Enter>.
Windows Setup
YouhavechosentocongureaSCSIAdapterforusewithWindows,
using a device support disk provided by an adapter manufacturer.
Select the SCSI Adapter you want from the following list, or press ESC
to return to the previous screen.
AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x86 platform
AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x64 platform
ENTER=Select F3=Exit
Figure 2
Step 3:
On the next screen, press <Enter> to continue the driver installation. After the driver installation, you can pro-
ceed with the Windows XP installation.
Appendix - 84 -
B. Installing Windows Vista
(The procedure below assumes that only one RAID array exists in your system.)
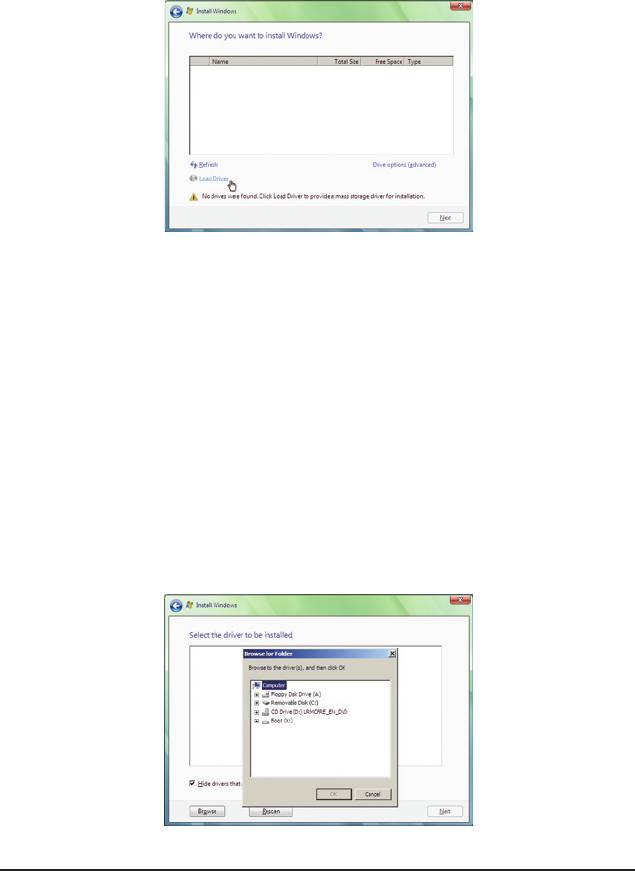
Step 1:
Restart your system to boot from the Windows Vista setup disk and perform standard OS installation steps.
When a screen similar to that below appears (RAID hard drive will not be detected at this stage), select Load
Driver (Figure 3).
Figure 3
Step 2:
Insert the motherboard driver disk (Method A) or the removable storage device such as USB ash drive that
contains the SATA RAID/AHCI driver (Method B), then specify the location of the driver (Figure 4). Note: For
users using a SATA optical drive, be sure to copy the driver les from the motherboard driver disk to a USB
ash drive before installing Windows Vista (go to the BootDrv folder and save the whole SB750V folder to
the USB ash drive). Then use Method B to load the driver.
Method A:
Insert the motherboard driver disk into your system and browse to the following directory:
\BootDrv\SB750V\LH
For Windows Vista 64-bit, browse to the LH64A folder.
Method B:
Insert the USB ash drive containing the driver les and browse to the LH (for Windows Vista 32-bit) or
LH64A (for Windows Vista 64-bit) folder.
Figure 4
- 85 - Appendix
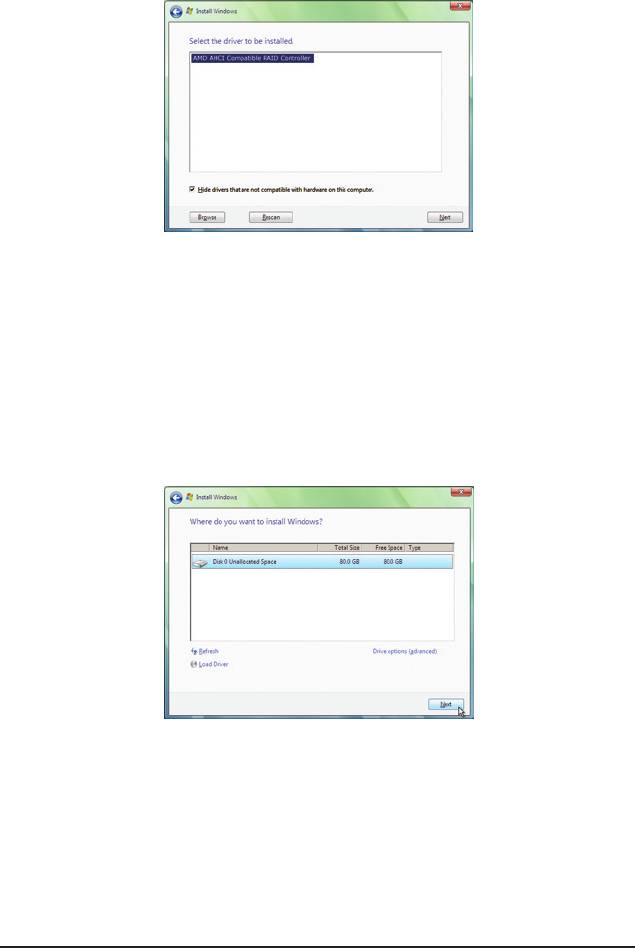
Step 3:
When a screen as shown in Figure 5 appears, select AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller and press
Next.
Figure 5
Step 4:
After the driver is loaded, the RAID drive will appear. Select the RAID drive and then press Next to continue
the OS installation (Figure 6).
Figure 6
Appendix - 86 -
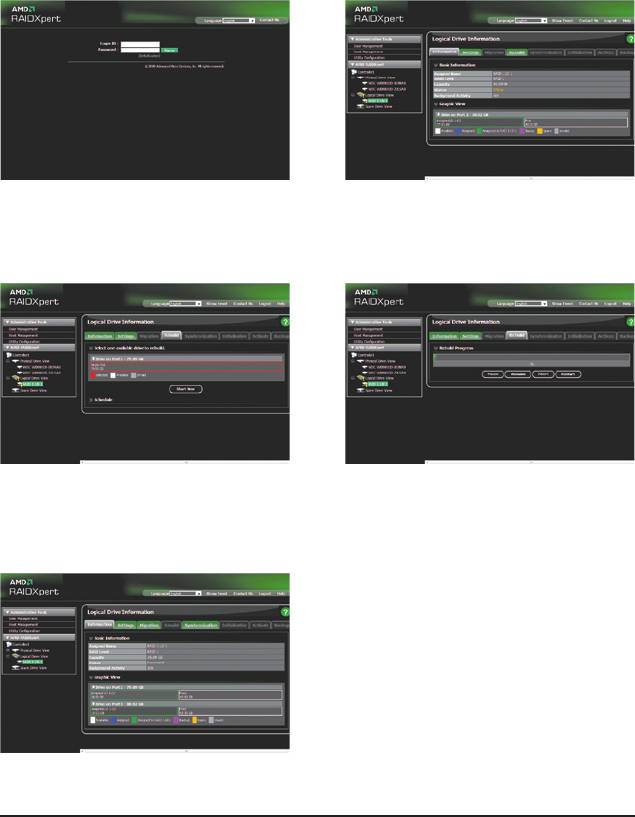
Rebuilding an Array:
Rebuilding is the process of restoring data to a hard drive from other drives in the array. Rebuilding applies
only to fault-tolerant arrays such as RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 10 arrays. To replace the old drive, make sure
to use a new drive of equal or greater capacity. The procedures below assume a new drive is added to re-
place a failed drive to rebuild a RAID 1 array.
While in the operating system, make sure the chipset drivers and ATi RAID Utility have been installed from
the motherboard driver disk. Then launch the AMD RAIDXpert from All Programs in the Start Menu.
Step 1:
Step 2:
Enter the login ID and password (default: "admin"),
Select the RAID array to be rebuilt under Logical
and then click Sign in to launch AMD RAIDXpert.
Drive View and click the Rebuild tab in the Logi-
cal Drive Information pane.
Step 3:
Step 4:
Select one available drive and click Start Now to
The rebuilding progress is displayed on the
start the rebuilding process.
screen and you can select Pause/Resume/
Abort/Restart during the rebuilding process.
Step 5:
When done, the array's status on the Information page
in the Logical Drive Information pane will display as
Functional.
- 87 - Appendix
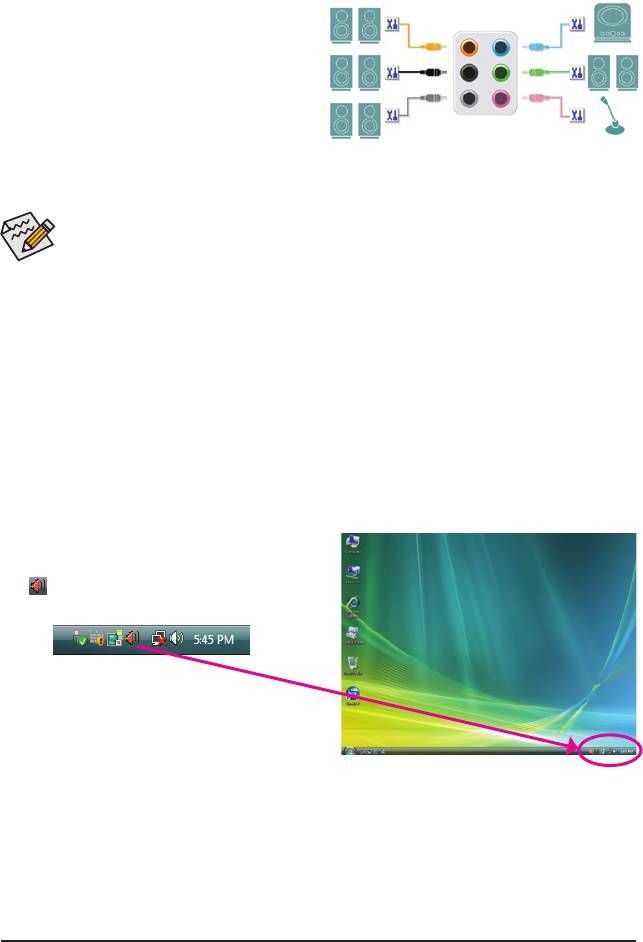
5-2 Conguring Audio Input and Output
5-2-1 Conguring 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio
The motherboard provides six audio jacks on the back
(Note)
panel which support 2/4/5.1/7.1-channel
audio.
The picture to the right shows the default audio jack
Center/Subwoofer
Line In
Speaker Out
assignments.
Rear Speaker Out Front Speaker Out
The integrated HD (High Definition) audio provides
Side
Mic In
jack retasking capability that allows the user to change
Speaker Out
the function for each jack through the audio driver.
For example, in a 4-channel audio conguration, if a Side speaker is plugged into the default Center/Sub-
woofer speaker out jack, you can retask the Center/Subwoofer speaker out jack to be Side speaker out.
• To install a microphone, connect your microphone to the Mic in jack and manually congure the
jack for microphone functionality.
• Audio signals will be present on both of the front and back panel audio connections simultane-
ously. If you want to mute the back panel audio (only supported when using an HD front panel
audio module), refer to instructions on the next page.
High Denition Audio (HD Audio)
HD Audio includes multiple high quality digital-to-analog converters (DACs) that support 44.1KHz/48KHz/
96KHz/192KHz sampling rate. HD Audio features multistreaming capabilities that allow multiple audio
streams (in and out) to be simultaneously processed. For example, users can listen to MP3 music, have an
Internet chat, make a telephone call over the Internet, and etc. all at the same time.
A. Conguring Speakers
(The following instructions use Windows Vista as the example operating system.)
Step 1:
After installing the audio driver, the HD Audio Manager
icon will appear in the notication area. Double-click
the icon to access the HD Audio Manager.
(Note) 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio Congurations:
Refer to the following for multi-channel speaker congurations.
• 2-channel audio: Headphone or Line out.
• 4-channel audio: Front speaker out and Rear speaker out.
• 5.1-channel audio: Front speaker out, Rear speaker out, and Center/Subwoofer speaker out.
• 7.1-channel audio: Front speaker out, Rear speaker out, Center/Subwoofer speaker out, and Side speaker out.
Appendix - 88 -
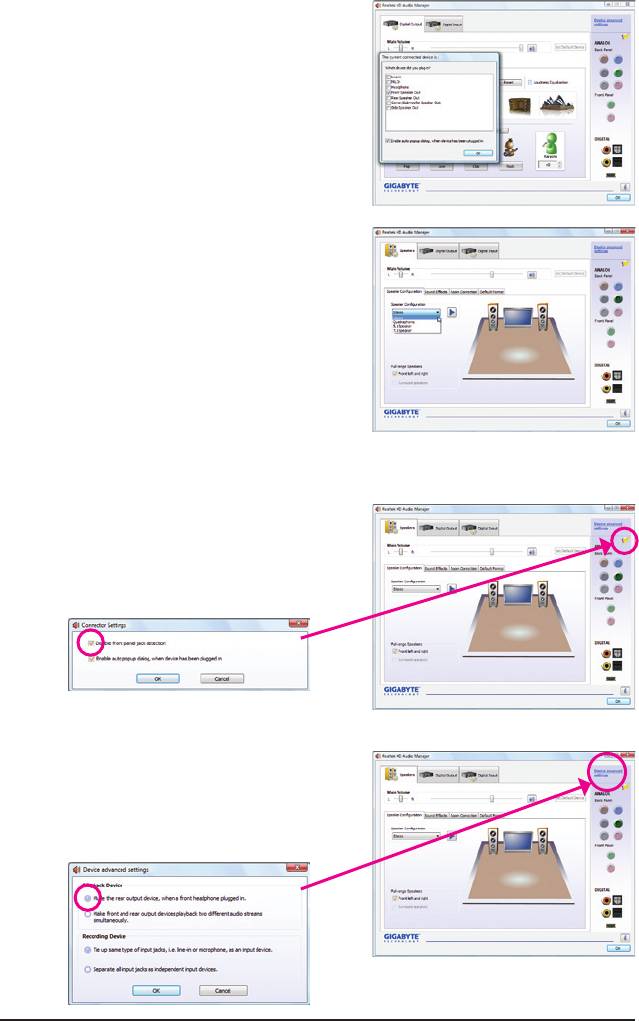
Step 2:
Connect an audio device to an audio jack. The The cur-
rent connected device is dialog box appears. Select the
device according to the type of device you connect. Then
click OK.
Step 3:
On the Speakers screen, click the Speaker Congura-
tion tab. In the Speaker Conguration list, select Stereo,
Quadraphonic, 5.1 Speaker, or 7.1 Speaker according to
the type of speaker conguration you wish to set up. Then
the speaker setup is completed.
B. Conguring Sound Effect
You may congure an audio environment on the Sound Effects tab.
C. Activating an AC'97 Front Panel Audio Module
If your chassis provides an AC'97 front panel audio mod-
ule, to activate the AC'97 functionality, click the tool icon
on the Speaker Configuration tab. On the Connector
Settings dialog box, select the Disable front panel jack
detection check box. Click OK to complete.
D. Muting the Back Panel Audio (For HD Audio Only)
Click Device advanced settings on the top right corner
on the Speaker Configuration tab to open the Device
advanced settings dialog box. Select the Mute the rear
output device, when a front headphone plugged in
check box. Click OK to complete.
- 89 - Appendix
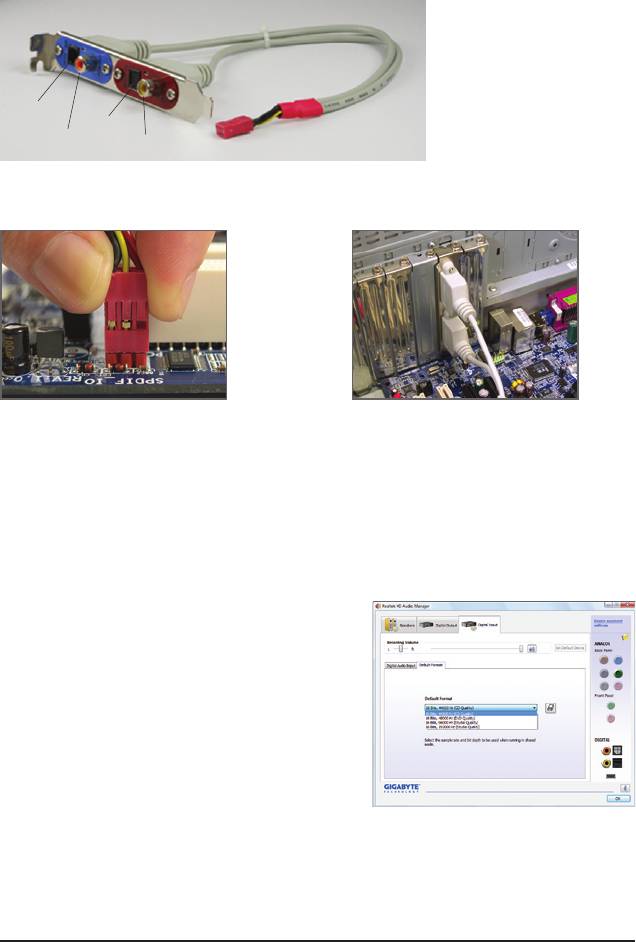
5-2-2 Conguring S/PDIF In/Out
The S/PDIF In and Out cable (optional) provides S/PDIF In and S/PDIF Out functionalities.
Optical
S/PDIF Out
Optical
Coaxial
S/PDIF In
Coaxial
S/PDIF Out
S/PDIFIn
A. Installing the S/PDIF In and Out Cable:
Step 1:
Step 2:
First, attach the connector at the end of the cable
Secure the metal bracket to the chassis back
to the SPDIF_IO header on your motherboard.
panel with a screw.
B. Conguring S/PDIF In:
The S/PDIF In jacks on the SPDI/F In and Out cable allow you to input digital audio signals to the computer
for audio processing.
Step:
After connecting the S/PDIF In device, access the Digital In-
put screen. Click the Default Format tab to select the default
format. Click OK to complete.
(Note) The actual locations of the SPDIF In and SPDIF Out connectors may differ by model.
Appendix - 90 -
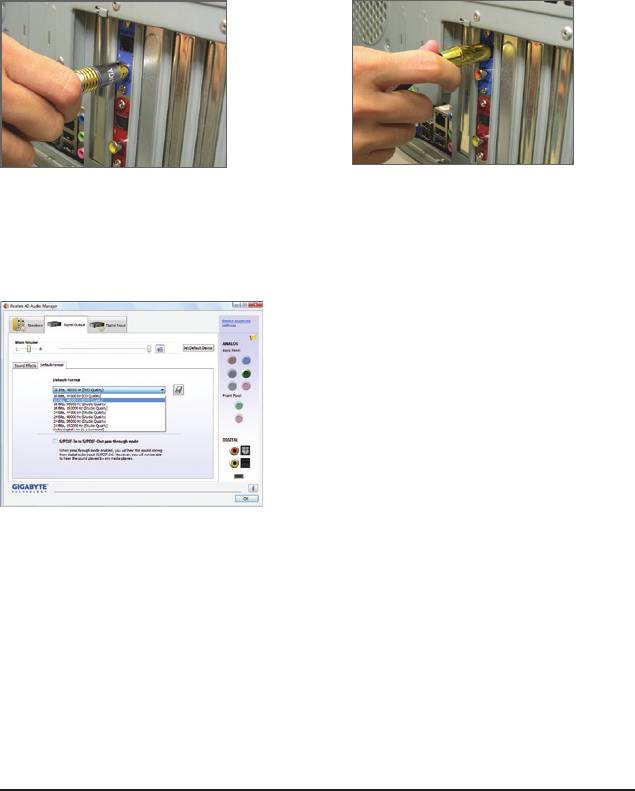
C. Conguring S/PDIF Out:
The S/PDIF out jacks can transmit audio signals to an external decoder for decoding to get the best audio
quality. Install the S/PDIF in and out cable (or connect a S/PDIF optical cable to the optical S/PDIF out con-
nector on the motherboard back panel) if you want to output S/PDIF digital audio signals to an external de-
coder.
C-1. Connecting a S/PDIF Out Cable:
Step:
Connect a S/PDIF coaxial cable or a S/PDIF optical cable (either one) to an external decoder for transmitting
the S/PDIF digital audio signals.
S/PDIF Coaxial Cable S/PDIF Optical Cable
C-2. Conguring S/PDIF Out:
Step:
On the Digital Output screen, click the Default Format tab and then select the sample rate and bit depth.
Click OK to complete.
- 91 - Appendix
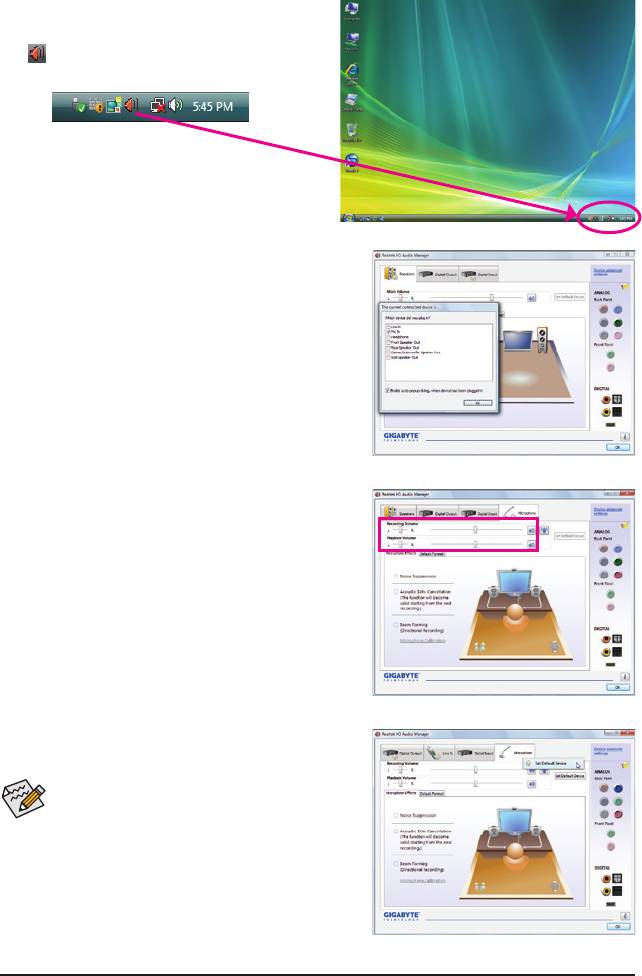
5-2-3 Conguring Microphone Recording
Step 1:
After installing the audio driver, the HD Audio Manager
icon will appear in the notication area. Double-click
the icon to access the HD Audio Manager.
Step 2:
Connect your microphone to the Mic in jack (pink) on
the back panel or the Mic in jack (pink) on the front
panel. Then congure the jack for microphone function-
ality.
Note: The microphone functions on the front panel and
back panel cannot be used at the same time.
Step 3:
Go to the Microphone screen. Do not mute the record-
ing volume, or you'll not be able to record the sound.
To hear the sound being recorded during the recording
process, do not mute the playback volume. It is recom-
mended that you set the volumes at a middle level.
If you want to change the current sound input
default device to microphone, right-click on Mi-
crophone and select Set Default Device.
Appendix - 92 -
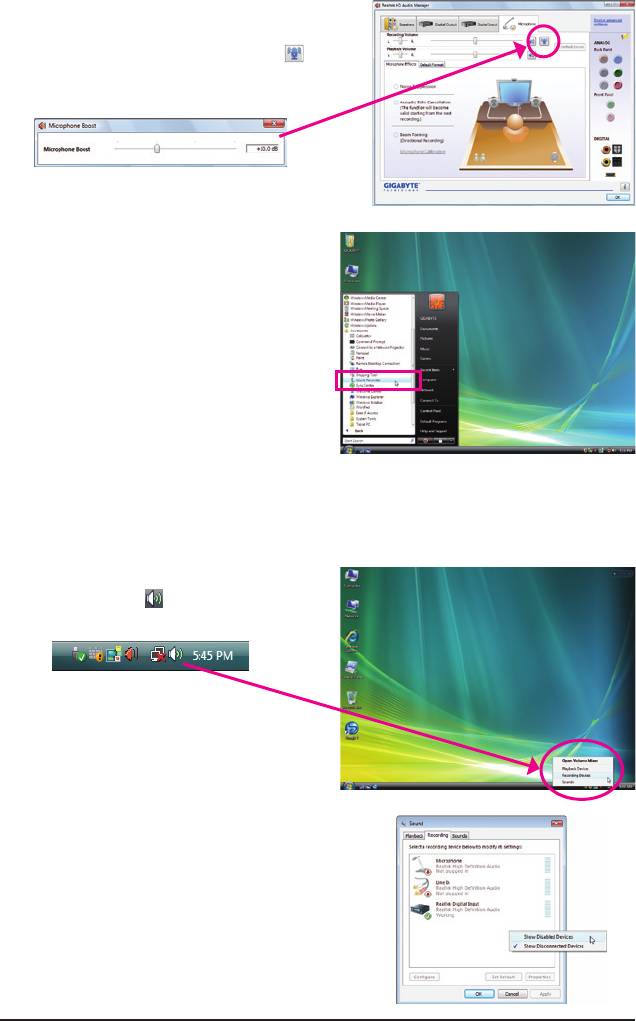
Step 4:
To raise the recording and playback volume for the
microphone, click the Microphone Boost icon on
the right of the Recording Volume slider and set the
Microphone Boost level.
Step 5:
After completing the settings above, click Start, point
to All Programs, point to Accessories, and then click
Sound Recorder to begin the sound recording.
* Enabling Stereo Mix
If the HD Audio Manager does not display the recording device you wish to use, refer to the steps below. The
following steps explain how to enable Stereo Mix (which may be needed when you want to record sound from
your computer).
Step 1:
Locate the Volume icon in the notication area and
right-click on this icon. Select Recording Devices.
Step 2:
On the Recording tab, right-click on an empty space
and select Show Disabled Devices.
- 93 - Appendix
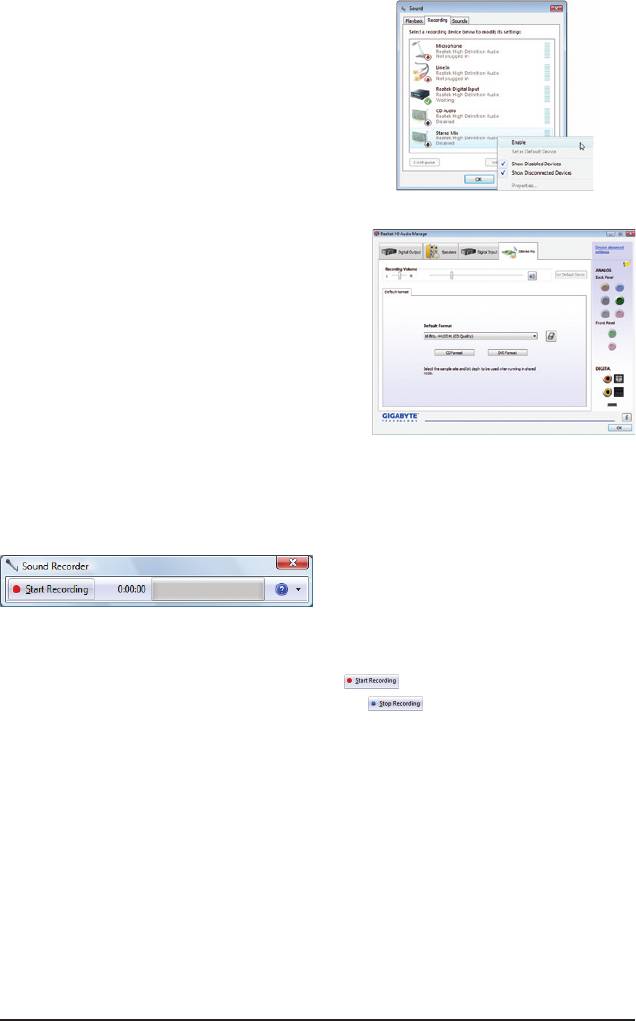
Step 3:
When the Stereo Mix item appears, right-click on this
item and select Enable. Then set it as the default de-
vice.
Step 4:
Now you can access the HD Audio Manager to cong-
ure Stereo Mix and use Sound Recorder to record the
sound.
5-2-4 Using the Sound Recorder
A. Recording Sound
1. Make sure you have connected the sound input device (e.g. microphone) to the computer.
2. To record the audio, click the Start Recording button .
3. To stop recording audio, click the Stop Recording button .
Be sure to save the recorded audio le upon completion.
B. Playing the Recorded Sound
You can play your recording in a digital media player program that supports your audio le format.
Appendix - 94 -

5-3 Troubleshooting
5-3-1 Frequently Asked Questions
To read more FAQs for your motherboard, please go to the Support&Downloads\Motherboard\FAQ page on
GIGABYTE's website.
Q: In the BIOS Setup program, why are some BIOS options missing?
A: Some advanced options are hidden in the BIOS Setup program. Press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup during the POST. In
the Main Menu, press <Ctrl>+<F1> to show the advanced options.
Q: Why is the light of my keyboard/optical mouse still on after the computer shuts down?
A: Some motherboards provide a small amount of standby power after the computer shuts down and that's why the light is
still on.
Q: How do I clear the CMOS values?
A: For motherboards that have a CMOS_SW button, press this button to clear the CMOS values (before doing this, please
turn off the computer and unplug the power cord). For motherboards that have a clearing CMOS jumper, refer to the
instructions on the CLR_CMOS jumper in Chapter 1 to short the jumper to clear the CMOS values. If your board doesn't
have this jumper, refer to the instructions on the motherboard battery in Chapter 1. You can temporarily remove the bat-
tery from the battery holder to stop supplying power to the CMOS, which will clear the CMOS values after about one
minute.
Q: Why do I still get a weak sound even though I have turned my speaker to the maximum volume?
A: Make sure your speaker is equipped with an internal amplier. If not, try a speaker with power/amplier.
Q: Why cannot I install the onboard HD audio driver successfully? (For Windows XP only)
A: Step 1: First, make sure Service Pack 1 or Service Pack 2 has been installed (check in My Computer > Properties > Gen-
eral > System). If not, please update it from Microsoft's website. Then make sure the Microsoft UAA Bus Driver for
High Denition Audio has been installed successfully (check in My Computer > Properties > Hardware > Device
Manager > System Devices).
Step 2: Check if Audio Device on High Denition Audio Bus or Unknown device is present in Device Manager or
Sound, video, and game controllers. If yes, please disable this device. (If not, skip this step.)
Step 3: Then go back to My Computer > Properties > Hardware > Device Manager > System devices and right-click on
Microsoft UAA Bus Driver for High Denition Audio and select Disable and Uninstall.
Step 4: In Device Manager, right-click on the computer name and select Scan for hardware changes. When the Add
New Hardware Wizard appears, click Cancel. Then install the onboard HD audio driver from the motherboard
driver disk or download the audio driver from GIGABYTE's website to install.
For more details, go to the Support&Downloads\Motherboards\FAQ page on our website and search for "onboard HD
audio driver."
Q: What do the beeps emitted during the POST mean?
A: The following Award BIOS beep code descriptions may help you identify possible computer problems.
(For reference only.)
1 short: System boots successfully
1 long, 3 short: Keyboard error
2 short: CMOS setting error
1 long, 9 short: BIOS ROM error
1 long, 1 short: Memory or motherboard error
Continuous long beeps: Graphics card not inserted properly
1 long, 2 short: Monitor or graphics card error
Continuous short beeps: Power error
- 95 - Appendix
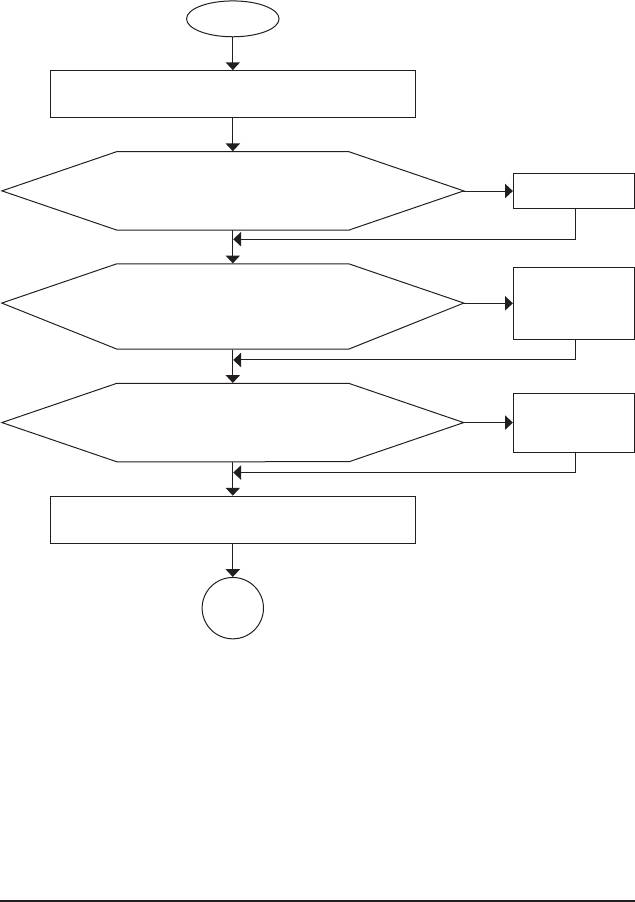
5-3-2 Troubleshooting Procedure
If you encounter any troubles during system startup, follow the troubleshooting procedure below to solve the
problem.
START
Turn off the power. Remove all peripherals, connecting cables, and
power cord etc.
Make sure the motherboard does not short-circuit with the chassis or
Yes
Isolate the short circuit.
other metal objects.
No
The problem is veried and solved.
Secure the CPU cooler
Check if the CPU cooler is attached to the CPU securely. Is the pow-
No
on the CPU. Connect the
er connector of the CPU cooler connected to the CPU_FAN header
CPU cooler power cable
properly?
to the motherboard.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
Correctly insert the
No
Check if the memory is installed properly on the memory slot.
memory into the memory
socket.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
Insert the graphics card. Connect the ATX main power cable and the
12V power cable. Turn on the power to start the computer.
Make sure the graphics card is securely seated in the
expansion slot and power connectors are rmly attached.
A
(Continued...)
Appendix - 96 -
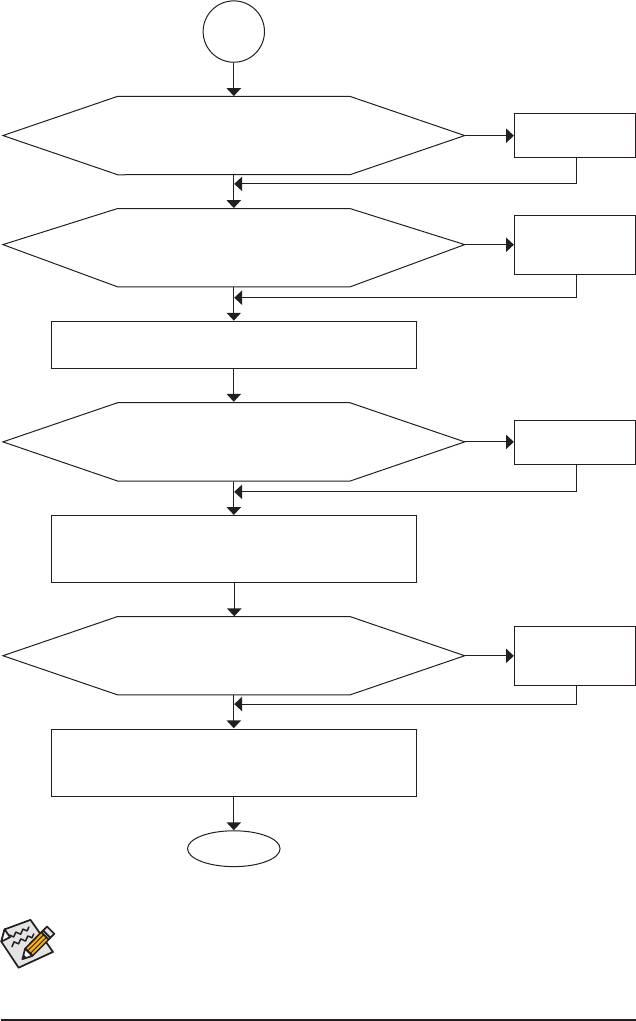
A
No
The power supply, CPU or
When the computer is turned on, is the CPU cooler running?
CPU socket might fail.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
The graphics card,
No
Check if there is display on your monitor.
expansion slot, or monitor
might fail.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
Turn off the computer. Plug in the keyboard and mouse and restart
the computer.
No
The keyboard or keyboard
Check if the keyboard is working properly.
connector might fail.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
Press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup. Select "Load Fail-Safe De-
faults" (or "Load Optimized Defaults"). Select "Save & Exit Setup" to
save changes and exit BIOS Setup.
The IDE/SATA device,
Turn off the computer and connect the IDE/SATA devices. Check if
No
connector, or cable might
the system can boot successfully.
fail.
Yes
The problem is veried and solved.
Reinstall the operating system. Reinstall other devices one by one
(install one device at one time and then boot the system to see if the
device works successfully).
END
If the procedure above is unable to solve your problem, contact the place of purchase or local
dealer for help. Or go to the Support&Downloads\Technical Service Zone page to submit your
question. Our customer service staff will reply you as soon as possible.
- 97 - Appendix
5-4 Regulatory Statements
Regulatory Notices
This document must not be copied without our written permission, and the contents there of must not be
imparted to a third party nor be used for any unauthorized purpose. Contravention will be prosecuted. We
believe that the information contained herein was accurate in all respects at the time of printing. GIGABYTE
cannot, however, assume any responsibility for errors or omissions in this text. Also note that the informa-
tion in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment by
GIGABYTE.
Our Commitment to Preserving the Environment
In addition to high-efciency performance, all GIGABYTE motherboards fulll European Union regulations
for RoHS (Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and WEEE
(Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) environmental directives, as well as most major worldwide safety
requirements. To prevent releases of harmful substances into the environment and to maximize the use of
our natural resources, GIGABYTE provides the following information on how you can responsibly recycle or
reuse most of the materials in your "end of life" product.
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive Statement
GIGABYTE products have not intended to add and safe from hazardous substances (Cd, Pb, Hg, Cr+6,
PBDE and PBB). The parts and components have been carefully selected to meet RoHS requirement. More-
over, we at GIGABYTE are continuing our efforts to develop products that do not use internationally banned
toxic chemicals.
Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive Statement
GIGABYTE will fulll the national laws as interpreted from the 2002/96/EC WEEE (Waste Electrical and Elec-
tronic Equipment) directive. The WEEE Directive species the treatment, collection, recycling and disposal of
electric and electronic devices and their components. Under the Directive, used equipment must be marked,
collected separately, and disposed of properly.
WEEE Symbol Statement
The symbol shown below is on the product or on its packaging, which indicates that this product
must not be disposed of with other waste. Instead, the device should be taken to the waste
collection centers for activation of the treatment, collection, recycling and disposal procedure.
The separate collection and recycling of your waste equipment at the time of disposal will help to
conserve natural resources and ensure that it is recycled in a manner that protects human health
and the environment. For more information about where you can drop off your waste equipment for recycling,
please contact your local government ofce, your household waste disposal service or where you purchased
the product for details of environmentally safe recycling.
When your electrical or electronic equipment is no longer useful to you, "take it back" to your local or
regional waste collection administration for recycling.
If you need further assistance in recycling, reusing in your "end of life" product, you may contact us at the
Customer Care number listed in your product's user's manual and we will be glad to help you with your
effort.
Appendix - 98 -
Finally, we suggest that you practice other environmentally friendly actions by understanding and using the
energy-saving features of this product (where applicable), recycling the inner and outer packaging (including
shipping containers) this product was delivered in, and by disposing of or recycling used batteries properly.
With your help, we can reduce the amount of natural resources needed to produce electrical and electronic
equipment, minimize the use of landlls for the disposal of "end of life" products, and generally improve our
quality of life by ensuring that potentially hazardous substances are not released into the environment and
are disposed of properly.
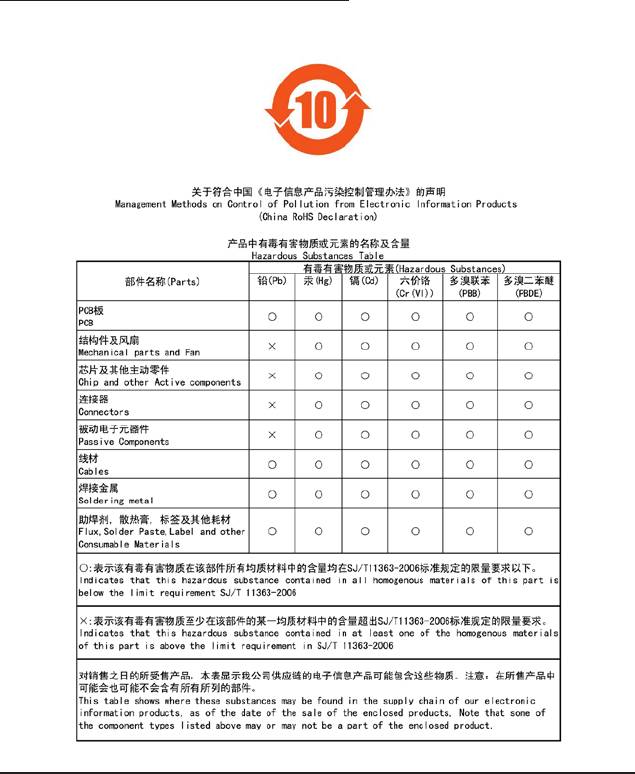
China Restriction of Hazardous Substances Table
The following table is supplied in compliance with China's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (China
RoHS) requirements:
- 99 - Appendix

Appendix - 100 -

- 101 - Appendix

Appendix - 102 -

Contact Us
• GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
• NINGBO G.B.T. TECH. TRADING CO., LTD. - China
Address: No.6, Bau Chiang Road, Hsin-Tien,
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.cn
Taipei 231, Taiwan
Shanghai
TEL: +886-2-8912-4000
TEL: +86-21-63410999
FAX: +886-2-8912-4003
FAX: +86-21-63410100
Tech. and Non-Tech. Support (Sales/Marketing) :
Beijing
http://ggts.gigabyte.com.tw
TEL: +86-10-62102838
WEB address (English): http://www.gigabyte.com.tw
FAX: +86-10-62102848
WEB address (Chinese): http://www.gigabyte.tw
Wuhan
• G.B.T. INC. - U.S.A.
TEL: +86-27-87851061
TEL: +1-626-854-9338
FAX: +86-27-87851330
FAX: +1-626-854-9339
GuangZhou
Tech. Support:
TEL: +86-20-87540700
http://rma.gigabyte.us
FAX: +86-20-87544306
Web address: http://www.gigabyte.us
Chengdu
• G.B.T. INC (USA) - Mexico
TEL: +86-28-85236930
Tel: +1-626-854-9338 x 215 (Soporte de habla hispano)
FAX: +86-28-85256822
FAX: +1-626-854-9339
Xian
Correo: soporte@gigabyte-usa.com
TEL: +86-29-85531943
Tech. Support:
FAX: +86-29-85510930
http://rma.gigabyte.us
Shenyang
Web address: http://latam.giga-byte.com
TEL: +86-24-83992901
• Giga-Byte SINGAPORE PTE. LTD. - Singapore
FAX: +86-24-83992909
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.sg
• GIGABYTE TECHNOLOGY (INDIA) LIMITED - India
• Thailand
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.in
WEB address : http://th.giga-byte.com
• Saudi Arabia
• Vietnam
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.com.sa
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.vn
• Gigabyte Technology Pty. Ltd. - Australia
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.com.au
- 103 - Appendix

• G.B.T. TECHNOLOGY TRADING GMBH - Germany
• Hungary
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.de
WEB address : http://www.giga-byte.hu
• G.B.T. TECH. CO., LTD. - U.K.
• Turkey
WEB address : http://www.giga-byte.co.uk
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.com.tr
• Giga-Byte Technology B.V. - The Netherlands
• Russia
WEB address : http://www.giga-byte.nl
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.ru
• GIGABYTE TECHNOLOGY FRANCE - France
• Poland
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.fr
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.pl
• Sweden
• Ukraine
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.se
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.ua
• Italy
• Romania
WEB address : http://www.giga-byte.it
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.com.ro
• Spain
• Serbia
WEB address : http://www.giga-byte.es
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.co.rs
• Greece
• Kazakhstan
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.com.gr
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.kz
• Czech Republic
You may go to the GIGABYTE website, select your language
WEB address : http://www.gigabyte.cz
in the language list on the top right corner of the website.
• GIGABYTE Global Service System
To submit a technical or non-technical (Sales/Market-
ing) question, please link to:
http://ggts.gigabyte.com.tw
Then select your language to enter the system.
Appendix - 104 -






