Citizen SRP-285N: Mode 0 - MAIN
Mode 0 - MAIN: Citizen SRP-285N

E – 11
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
Mode 0 - MAIN
Arithmetic Calculations
z
Arithmetic operations are performed by pressing the keys in the
same sequence as in the expression. See Example 6.
z
For negative values, press [ (
−
) ] before entering the value. See
Example 7.
z
For mixed arithmetic operations, multiplication and division are
given priority over addition and subtraction. See Example 8.
z
Results greater than 10
10
or less than 10
-9
are displayed in
exponential form. See Example 9.
Display formats
z
Decimal places formats are selected by pressing [ 2nd ] [ TAB ] to
display the menu. To set decimal places to
n
(
F0123456789
),
enter a
n
value directly or press [
] key while the item is
underlined. (The default setting is floating point notation
F
and the
n
value is
•
). See Example 10.
z
Even if the number of decimal places is specified, internal
calculation for a mantissa is performed up to 24 digits, and the
display value is stored in 10 digits. To round off those values to
the specified number of decimal places, press [ 2nd ] [ RND ].
See Example 11~12.
z
Number display formats are selected by pressing [ 2nd ]
[ SCI/ENG ] to display the menu. The items on the menu are
FLO
(for floating point),
SCI
( for scientific), and
ENG
(for engineering).
Press [ ] or [ ] until the desired formats is underlined, and
then press [
]. See Example 13.
(Note) : The engineering format is similar to the scientific format,
except the mantissa can have up to three digits left of
the decimal, instead of only one, and the exponent is
always a multiple of three. It is useful for engineers to
convert units based on multiples of 10
3
.
z
You can enter a number in mantissa and exponent form by [ EXP ]
key. See Example 14.
Parentheses Calculation
z
Operations inside parentheses are always executed first. The
calculator can use up to 13 levels of consecutive parentheses in a
single calculation. See Example 15.
z
Closed parentheses occurring immediately before operation of the
[
] key may be omitted, no matter how many are required.
See Example 16.

E – 12
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
z
A multiplication sign " x " occurring immediately before an open
parenthesis can omitted. See Example 17.
(Note) : The calculator can auto-correct abbreviated
multiplication in front of all functions, except memory
variables, left parenthesis, type B functions.
z
Henceforth, abbreviated type will not be used in this manual.
See Example 18.
z
The correct result cannot be derived by entering [ ( ] 2 [ + ] 3 [ ) ]
[ EXP ] 2. Be sure to enter [ x ] 1 between the [ ) ] and [ EXP ] in
the below example. See Example 19.
Percentage Calculation
z
[ 2nd ] [ % ] divides the number in the display by 100. You can use
this key sequence to calculate percentages, add-ons, discounts,
and percentages ratios. See Example 20~21.
Continuous calculation function
z
The calculator enables you to repeat the last operation executed
by pressing [
] key for further calculation. See Example
22.
z
Even if calculations are concluded with the [
] key, the
result obtained can be used for further calculation. See Example
23.
Answer Function
z
Answer function stores the most recently calculated result. It is
retained even after the power is turned off. Once a numeric value
or numeric expression is entered and [
] is pressed, the
result is stored by this function. See Example 24.
(Note) : Even if execution of a calculation results in an error,
however, Answer memory retains its current value.
Logarithm And Antilogarithm
z
The calculator can calculate common and natural logarithms and
anti-logarithms using [ log ], [ ln ], [ 2nd ] [ 10
x
], and [ 2nd ]
[ e
x
]. See Example 25~27.
Fraction Calculation
Fraction value display is as follow :
5 / 12
Display of
12
5
56
∪
5 /12
Display of 56
12
5

E – 13
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
z
To enter a mixed number, enter the integer part, press [ a
b
/
c
],
enter the numerator, press [ a
b
/
c
], and enter the denominator ; To
enter an improper fraction, enter the numerator, press [ a
b
/
c
], and
enter the denominator. See Example 28.
z
During a fraction calculation, if the figure is reducible, a figure is
reduced to the lowest terms after pressing a function command
key ( [ + ], [ – ], [ x ] or [ ] ) or the [
] key. By pressing
[ 2nd ] [ a
b
/
c
d
/
e
], the displayed value will be converted to the
improper fraction and vice versa. See Example 29.
z
To convert between a decimal and fractional result, press [ 2nd ]
[ F
D ] and [
]. See Example 30.
z
Calculations containing both fractions and decimals are calculated
in decimal format. See Example 31.
Angle Unit Conversion
z
The angle units (
DEG
,
RAD
,
GRAD
) is set by pressing [ DRG ] to
display the angle menu. The relation among the three angle units
is :
180
°
=
π
rad = 200 grad
Angle conversations ( See Example 32. ) :
1. Change the default angle settings to the units you want to
convert to.
2. Enter the value of the unit to convert.
3. Press [ DMS ] to display the menu. The units you can select
are
°
(degrees),
′
(minutes),
″
(seconds),
r
(radians),
g
(gradians) or DMS (Degrees-Minutes-Seconds).
4. Choose the units you are converting from.
5. Press [
] twice.
z
To convert an angle to
DMS
notation, select "
DMS
" which
converts an entry to
DMS
notations, i.e., where
1
°
30
′
0
″
represents 1 degrees, 30 minutes, 0 seconds. See Example 33.
z
To convert a
DMS
notation to decimal, select
°
(degrees),
′
(minutes),
″
(seconds). See Example 34.
E – 14
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
Trigonometric / Inverse-Tri. Functions
The calculator provides standard trigonometric functions and inverse
trigonometric functions - sin, cos, tan, sin
–1
, cos
–1
and tan
–1
. See
Example 35~37.
(Note) : When using those keys, make sure the calculator is set
for the angle unit you want.
Hyperbolic / Inverse-Hyp. Functions
The calculator uses [ 2nd ] [ HYP ] to calculate the hyperbolic
functions and inverse- hyperbolic functions – sinh, cosh, tanh,
sinh
–1
, cosh
–1
and tanh
–1
. See Example 38~39.
(Note) : When using those keys, make sure the calculator is set
for the angle unit you want.
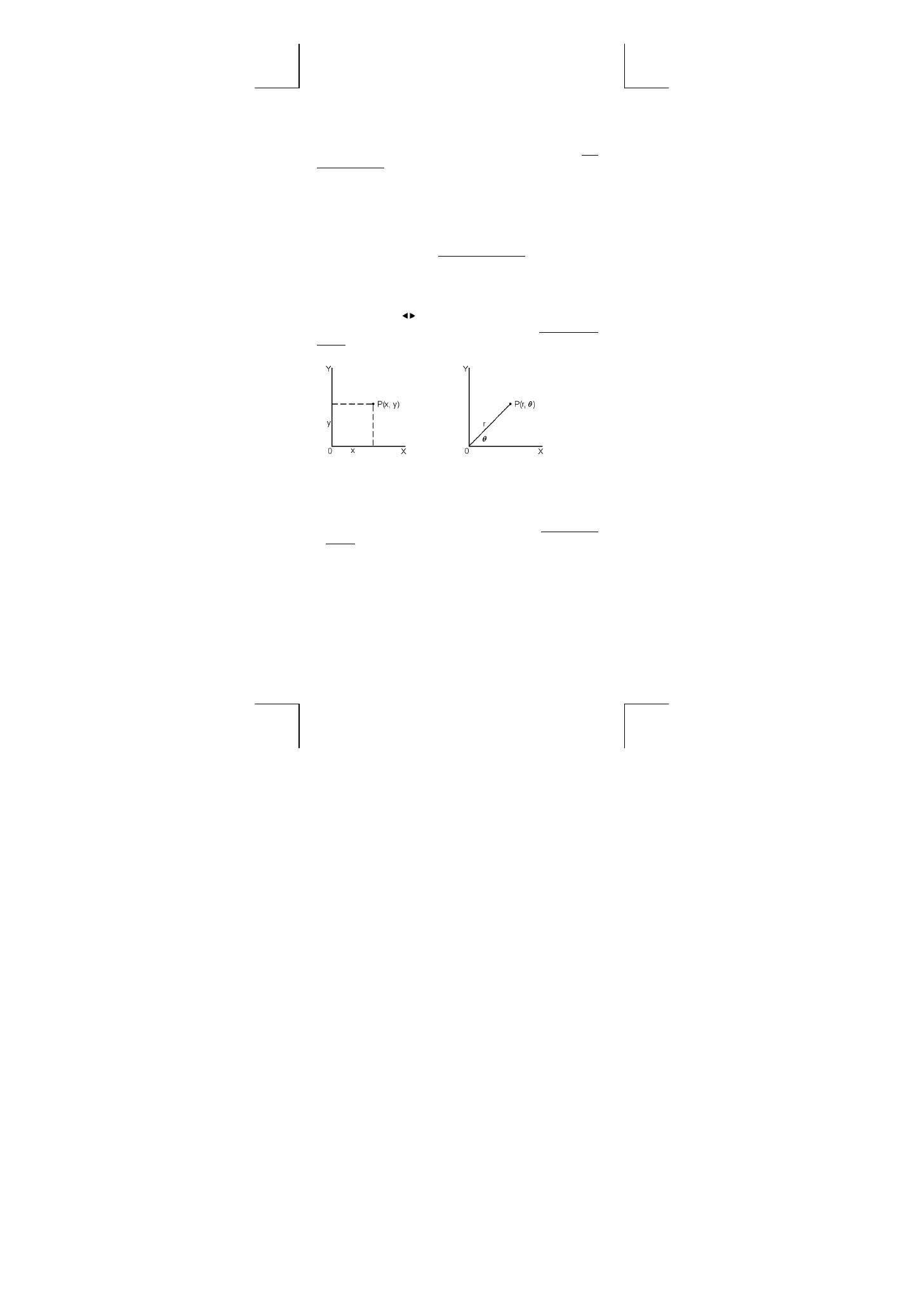
Coordinates Transformation
Pressing [ 2nd ] [ R
P ] displays a menu to convert rectangular
coordinates to polar coordinates or vice versa. See Example
40~41.
Rectangular Coordinates
Polar Coordinates
x + y i = r (cos
θ
+ i sin
θ
)
(Note) : When using those key, make sure the calculator is set
for the angle unit you want.
Probability
z
Pressing [ PRB ] displays the probability menu. See Example
42~46. With the following functions :
nPr
Calculates the number of possible permutations of n item
taken r at a time.
nCr
Calculates the number of possible combinations of n
items taken r at a time.
!
Calculates the factorial of a specified positive integer n ,
where n
≦
69.
RANDM
Generates a random number between 0 and 1.
RANDMI
Generates a random integer value between two specified
integers, A and B, where A
≦
random value
≦
B

E – 15
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
Other Functions ( x
–1
,
√
,
X
, x
2
, ^ )
z
The calculator also provides reciprocal ( [ x
–1
] ), square root
( [
√
] ), universal root ( [
X
] ), square ( [ x
2
] ) and
exponentiation ( [ ^ ] ) functions. See Example 47~50.
Unit Conversions
z
The calculator has a built-in unit conversion feature that enables
you to convert numbers from metric to English units and vice
versa. See Example 51.
1. Enter the number you want to convert.
2. Press [ 2nd ] [ CONV ] to display the menu. There are 7
menus, covering distance, area, temperature, capacity,
weight, energy, and pressure.
3. Use the [ ] [ ] to scroll through the list of units until a
appropriate units menu is shown, then [
].
4. Pressing
[ ] or [ ] can convert the number to another
unit.
Physical Constants
z
You can use a number of physical constants in your calculations.
See table below :
Symbol Meaning
Value
c
Speed of light in vacuum
299792458 m / s
g
Acceleration of gravity
9.80665 m.s
–2
G Gravitational
constant
6.6725985 x 10
–11
N.m
2
kg
–2
Vm
molar volume of ideal gas
0.0224141 m
3
mol
–1
NA
Avagadro's number
6.022136736 x 10
23
mol
–1
e
Elementary charge
1.6021773349 x 10
–19
C
me
Electron mass
9.109389754 x 10
–31
kg
mp
Proton mass
1.672623110 x 10
–27
kg
h
Plank's constant
6.626075540 x 10
–34
J.s
k
Boltzmann's constant
1.38065812 x 10
–23
J.K
–1
R
Gas constant
8.3145107 J / mol
z
k
F
Faraday constant
96485.30929 C / mol
mn
Neutron constant
1.67492861 x 10
–27
kg
µ
Atomic mass constant
1.66054021 x 10
–27
kg
ε
0
Dielectric permittivity
8.854187818 x 10
–12
F/m
µ
0
Magnetic permittivity
1.256637061 x 10
–6
H / m
φ
0
Flux quantum
2.0678346161 x 10
–15
Vs
a
0
Bohr radius
5.2917724924 x 10
–11
m
µB
Bohr magneton
9.274015431 x 10
–24
A
z
m
2
µN
Neutron magnetic moment
5.050786617 x 10
–27
J / T
Оглавление
- General Guide
- Before starting calculation
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guía GeneraI
- Antes de empezar los cálculos
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guia Geral
- Antes de começar cálculos
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Allgemeine Hinweise
- Vor dem Rechnen
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guide Général
- Avant de Commencer le Calcul
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guida Generale
- Prima di iniziare i calcoli
- Modalità 0- MAIN.
- Modalità 1 - STATISTICHE
- Modalità 2 - Base-n
- Modalità 3 - CPLX
- Algemene inleiding
- Modus 0 - MAIN
- Modus 1 - STAT
- Modus 2 - Base-n
- Modus 3 - CPLX
- Generel vejledning
- Inden du går i gang med at foretage beregninger
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Основное руководство
- Перед началом вычислений
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Instrukcja Obs ł ugi
- Przed u ż yciem
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Mode 5 - QE
- Petunjuk Umum
- Sebelum mulai menghitung
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Mode 5 - QE
- 一般操作說明
- 使用前說明
- 操作模式 0 - MAIN
- 操作模式 1 - STAT
- 操作模式 2 - Base-n
- 操作模式 4 - VLE

