Citizen SRP-285N: Mode 1 - STAT
Mode 1 - STAT: Citizen SRP-285N

E – 16
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
To insert a constant at the cursor position ( See Example 52. ) :
1. Press [ CONST ] to display the physical constants menu.
2. Press
[ ] until the constant you want is underlined.
3. Press
[
].
Mode 1 - STAT
There are three menu operations in statistics menu :
1–VAR
( for
analyzing data in a single dataset),
2–VAR
( for analyzing paired
data from two datasets ) and
D–CL
( for clearing all datasets). See
Example 38.
Single-Variable / Two-Variable Statistics
Step :
1. From the statistics menu, choose
1–VAR
or
2–VAR
and
press [
].
2. Press [ DATA ] and there are three menus:
DATA–INPUT
,
LIMIT–SET
,
DISTR
. Please select
DATA–INPUT
and press
[
].
3. Enter an x - value and press [ ].
4. Enter the frequency (
FREQ
) of the x - value (in
1–VAR
mode) or the corresponding y - value ( in
2–VAR
mode )
and press [ ].
5. To enter more data, repeat from step 3.
6. Press [ 2nd ] [ STATVAR ] and scroll through the statistical
result menus by [ ] or [ ] to find out statistical variables
you want. ( See table below )
Variable
Meaning
n
Number of the x values or x-y pairs entered.
or
Mean of the x values or y values
Xmax
or
Ymax
Maximum of the x values or y values
Xmin
or
Ymin
Minimum of the x values or y values
Sx
or
Sy
Sample standard deviation of x values or y
values.
1
n
)
x
x
(
S
2
x
−
∑
−
=
,
1
n
)
y
y
(
Sy
2
−
∑
−
=
σ
x
or
σ
y
Population standard deviation of x values or y
values
n
)
x
x
(
x
2
∑
−
=
σ
,
n
)
y
y
(
y
2
∑
−
=
σ
Σ
x
or
Σ
y
Sum of all x values or y values
E – 17
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
Σ
x
2
or
Σ
y
2
Sum of all x
2
values or y
2
values
Σ
x y
Sum of (x
z
y) for all x-y pairs
Process capability
Step : ( See Example 53~54. )
1. Press [ DATA ] and there are three menus :
DATA–INPUT
,
LIMIT–SET
,
DISTR
. Please select
LIMIT–SET
and press
[
].
2. Enter an upper spec. limit value (
X USL
or
Y USL
), then
press [ ].
3. Enter a lower spec. limit value (
X LSL
or
Y LSL
), then
press [
].
4. Enter the datasets you want under
DATA–INPUT
mode.
5. Press [ 2nd ] [ STATVAR ] and scroll through the statistical
results menu by [ ] or [ ] to find out process capability
variables you want. ( See table below )
Variable
Meaning
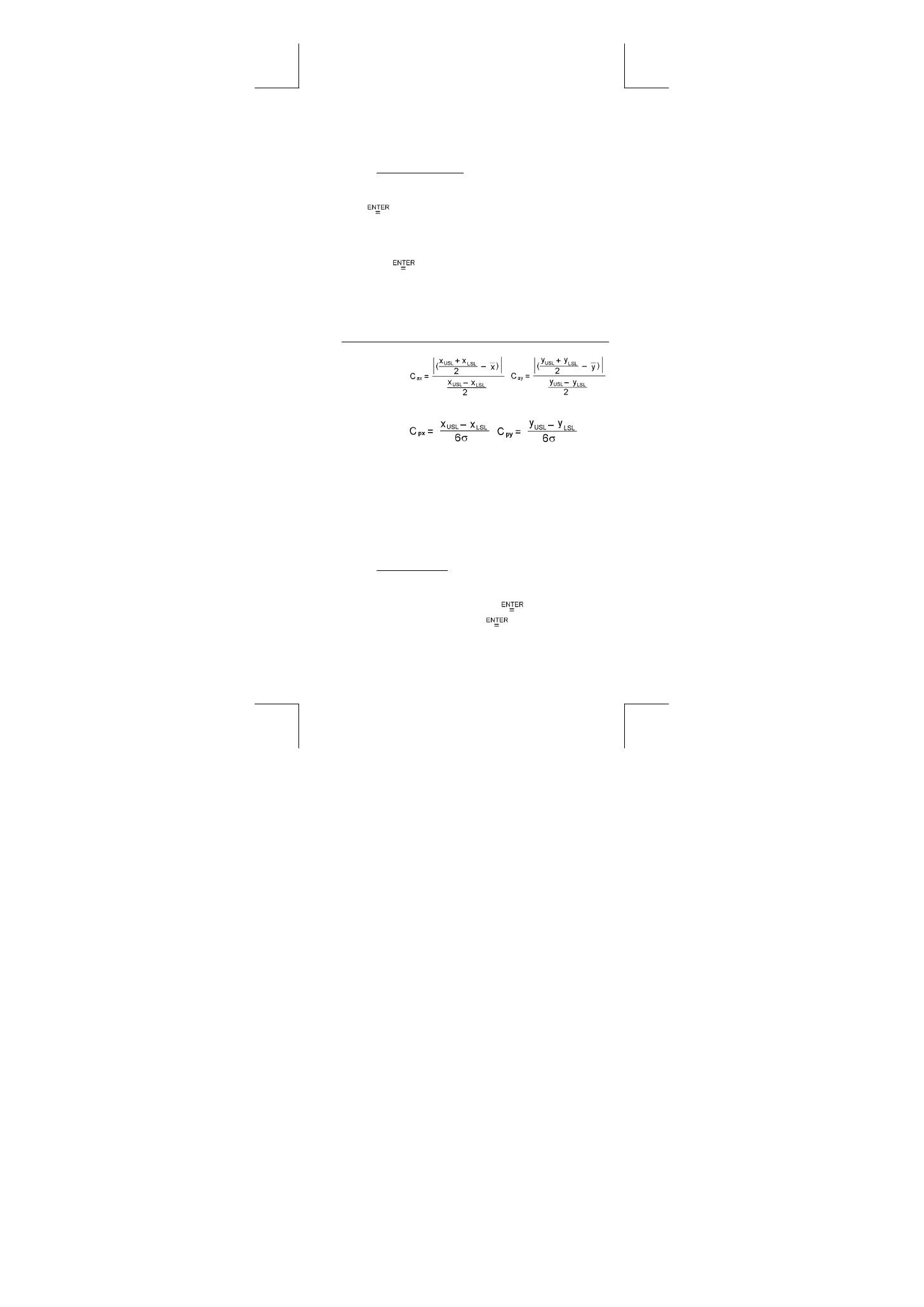
Cax
or
Cay
Capability accuracy of the x values or y values
,
Cpx
or
Cpy
Potential capability precision of the x values or y
values,
,
Cpkx
or
Cpky
Minimum (C
PU
, C
PL
) of the x values or y values,
where C
PU
is upper spec. limit of capability
precision and C
PL
is lower spec. limit of
capability precision
C
pkx
= Min (C
PUX
, C
PLX
) = C
px
(1 – C
ax
)
C
pky
= Min (C
PUY
, C
PLY
) = C
py
(1 – C
ay
)
(Note) : When calculating process capability in
2–VAR
mode, the
x
n
and y
n
are independent with each other.
Probability distribution
Step : ( See Example 55. )
1. Based on the datasets in
1–VAR
mode, press [ DATA ] and
there are three menu :
DATA–INPUT
,
LIMIT–SET
,
DISTR
.
Please choose
DISTR
and press [
].
2. Enter a
a
x
value, then press [
].
3. Press [ STATVAR ] and scroll through the statistical results
menu by [ ] or [ ] to find out probability distribution
variables you want. (See table below)

E – 18
File name : CBM_SR285,A_HDBSR285T19_English.doc
version : 2010/04/26
Variable
Meaning
t
Test
value
P ( t )
Represent the cumulative fraction of the
standard normal distribution that is less than the
value t
R ( t )
Represent the cumulative fraction of the
standard normal distribution that lies between
the value t and 0. R ( t ) =1 – ( t )
Q ( t )
Represent the cumulative fraction of the
standard normal distribution that is greater than
the value t Q ( t ) = | 0.5 – ( t ) |
Linear regression
Step : ( See Example 56. )
1. Based on the datasets in
2–VAR
mode, press [ STATVAR ]
and scroll through the statistical results menu by [ ] or [ ]
to find out
a
,
b
, or
r
.
2. To predict a value for x (or y) given a value for y (or x), select
the x ' (or y ' variable, press [
], enter the given value,
and press [
] again. (See table below)
Variable
Meaning
a
Linear regression y-intercept
∑
∑
−
=
x
n
b
y
a
b
Linear regression slope
∑
∑
−
∑
∑ ∑
−
=
)
)
x
(
x
n
(
)
y
x
xy
n
(
b
2
2
r
Correlation
coefficient
∑
∑
∑
∑
−
−
∑
∑ ∑
−
=
)
)
y
(
y
n
)(
)
x
(
x
n
(
)
y
x
xy
n
(
r
2
2
2
2
x '
Predicted x values given a, b, and y vales
b
a
y
'
x
−
=
y '
Predicted y value given a, b, and x value.
bx
a
'
y
+
=
Correcting data
Step : ( See Example 57. )
1. Press [ DATA ].
2. To change x - values or the frequency of the x - value in
1–VAR
mode ( or the corresponding y - value in
2–VAR
mode ), please choose
DATA–INPUT
. To change upper spec.
Оглавление
- General Guide
- Before starting calculation
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guía GeneraI
- Antes de empezar los cálculos
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guia Geral
- Antes de começar cálculos
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Allgemeine Hinweise
- Vor dem Rechnen
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guide Général
- Avant de Commencer le Calcul
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Guida Generale
- Prima di iniziare i calcoli
- Modalità 0- MAIN.
- Modalità 1 - STATISTICHE
- Modalità 2 - Base-n
- Modalità 3 - CPLX
- Algemene inleiding
- Modus 0 - MAIN
- Modus 1 - STAT
- Modus 2 - Base-n
- Modus 3 - CPLX
- Generel vejledning
- Inden du går i gang med at foretage beregninger
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Основное руководство
- Перед началом вычислений
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Instrukcja Obs ł ugi
- Przed u ż yciem
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Mode 5 - QE
- Petunjuk Umum
- Sebelum mulai menghitung
- Mode 0 - MAIN
- Mode 1 - STAT
- Mode 2 - Base-n
- Mode 3 - CPLX
- Mode 5 - QE
- 一般操作說明
- 使用前說明
- 操作模式 0 - MAIN
- 操作模式 1 - STAT
- 操作模式 2 - Base-n
- 操作模式 4 - VLE

