Assistant AC–3252: инструкция
Раздел: Электроника
Тип: Калькулятор
Инструкция к Калькулятору Assistant AC–3252
SCIENTIFIC
CALCULATOR
MODEL
AC-3252
ENG
DEU
RUS
UKR
OPERATION MANUAL
WWW.TIWELL.COM
WWW.ASSISTANT.UA
Made in China
Stamp Печать магазина
Date of sale Дата продажи
Model Номер модели
Warranty period Гарантийный срок

...YOUR ASSISTANTS
OPERATING RULES
Thank you for purchasing the Scientifi c Calculator.
To ensure trouble-free operation, please bear in mind the following:
1. Do not carry the calculator in the back pocket of trousers.
2. Do not drop it or apply excessive forces.
3. Do not expose the calculator to damp, dusty circumstances or big
temperature fl uctuation.
4. Clean only with a soft dry cloth.
WARNING! Before using the calculator, be sure to read the instructions
thoroughly. And please keep this manual for future reference.
WARNING! When exposed to a strong electric fi eld or shock during
use, the calculator may perform abnormal. To restore normal operation
press [RESET] key on the back of the calculator. Note that with this
operation everything in the memory will be erased.
E
p. 1

CONTENTS
I. MAIN FEATURES ...............................................................................5
II. DISPLAY ............................................................................................6
1. Two-tier Display ..........................................................................6
2. Display Symbols .........................................................................6
3. Exponential Display ....................................................................7
III. OPERATION CONTROL ..................................................................7
IV. BEFORE USING THE CALCULATOR ...........................................16
1. Mode Selection ........................................................................16
2. Angle Unit Defi nition .................................................................17
3. Number Display System Defi nition ...........................................17
1) «FIX» Mode ..................................................................................17
2) «SCI» Mode ................................................................................. 17
3) «ENG» Mode ............................................................................... 17
4. Calculation Range ....................................................................18
5. Inputting Character Number .....................................................18
6. Special Functions .....................................................................19
1) Omitting the Multiplication Sign ...................................................19
E
2) Replay Function ...........................................................................19
3) Answer Function...........................................................................19
4) Continuous Calculation Function ................................................20
7. Error Information ......................................................................20
8. Calculation Priority ...................................................................21
p. 2
VII. ЗАМІНА ДЖЕРЕЛА ЖИВЛЕННЯ
При зниженні контрастності дисплею необхідно замінити елемент
живлення. Для цього:
1. Вимкніть калькулятор.
2. Відкрутіть кришку відсіку джерела живлення.
3. Витягніть старий елемент живлення та встановіть новий.
4. Закрийте кришку джерела живлення, після чого натисніть кнопки
[OFF] та [ON/C] для проведення обчислень.
U
стор. 48
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
V. SIENTIFIC CALCULATIONS ...........................................................22
1. Basic Calculations ....................................................................22
2. Scientifi c Function Calculations ...............................................23
1) Power/root:
E
p. 3
3
,
2
-1
x
, x
, x
,
y ............................................23
2) Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions ..........23
3) Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions ....................24
4) Logarithmic and Exponential Functions .............................24
5) Factorial, Permutation and Combination ............................24
6) Coordinate Conversion ......................................................25
7) Percentage and Random ...................................................25
8) Decimal and Hexadecimal Calculations .............................26
9) Angular Unit Conversion ....................................................26
3. Memory Functions and Calculations ........................................27
1) Independent Memory (MR) ................................................27
2) Variable Memories..............................................................28
3) Constant Memories ............................................................28
4. Fraction Calculations ................................................................29
5. «Base-N» Calculations .............................................................30
1) Valid Values in Each Number System ................................30
2) Number of Digits Displayed in Each Number System ........30
3) Calculation Range ..............................................................30
4) Binary and Octal Block Display ..........................................31
5) Binary, Octal, Decimal and Hexadecimal Conversions ......32
6) Basic Arithmetic Operations Using Binary, Octal, Decimal
and Hexadecimal Values .................................................32
7) Logical Operations .............................................................33
6. Statistical Calculations .............................................................33
1) Data Input ...........................................................................33
2) Input Data Delete ...............................................................34
3) Statistical Calculation Formulas .........................................34
4) Statistical Calculation Examples ........................................35
7. Formula Calculations ...............................................................35
1) Built-in Formulas ................................................................35
2) Formula Search ..................................................................38
3) Storing User Formulas .......................................................38
4) Deleting User Formulas .....................................................38
5) Formula Calculations .........................................................39
VI. RANGE OF FUNCTION INPUT .....................................................40
VII. BATTERY REPLACEMENT ..........................................................42
E
p. 4
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
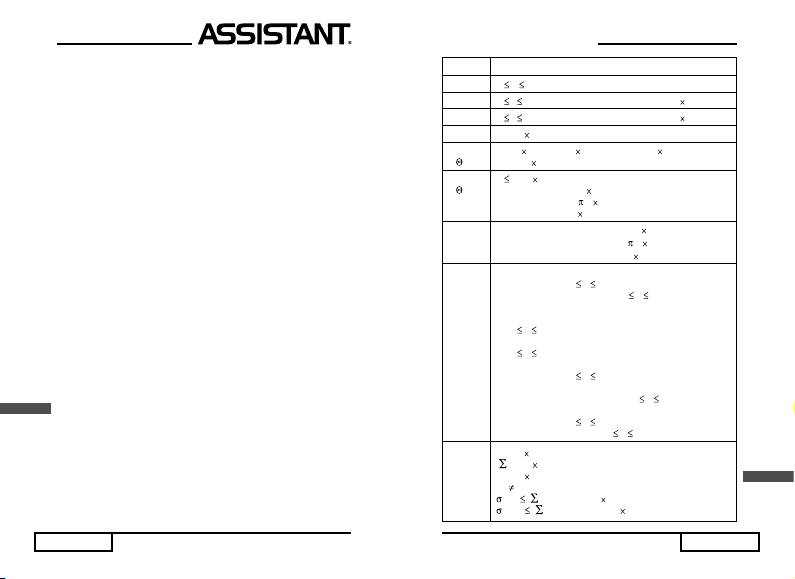
Функції Допустимі значення аргументу функцій
n! 0 n 69, де n – цілі числа
100
nPr, 0
r n, де n, r – цілі числа; результат < 1 10
100
nCr 0 r n, де n, r – цілі числа; результат < 1 10
7
→ DEG [х] < 1 10
100
100
2
2
x, y →
|x| <1 10
,|y| <1 10
, (x
+ y
) < 1 10100,
100
r,
|y/x| < 1
10
100
0
r < 1 10
10
r, →
Градуси (D): | X | < 1 10
98
х, у
Радіани (R): | X | < /2 10
100
Гради (G): | X | < 1 10
100
Градуси (D) → Радіани (R): |x| <1 10
98
DRG →
Радіани (R) → Гради (G): |x| <
/2 10
100
Гради (G) → Градуси (D): |x| <1 10
→DEC
У десятковій системі числення (DEC):
Додатні числа: 0 х
2147483647
Від’ємні числа: –2147483647 х –1
→ BIN
У двійковій системі числення (BIN):
Додатні числа:
0
х 01111111111111111111111111111111
Від’ємні числа:
0 х -111111111111111111111111111111111
→ OCT
У вісімковій системі числення (OCT):
Додатні числа: 0
х 17777777777
Від’ємні числа:
20000000000 х 37777777777
→ НЕХ
У шістнадцятковій системі числення (HEX):
Додатні числа: 0
х 7FFFFFFF
Від’ємні числа: 80000000 х
FFFFFFFF
50
|x| < 1 10
100
| x| < 1 10
100
|n| < 1 10
STAT
U
x:n 0
2
2
100
: 0 ( x
- nx
) / n < 1 10
, n>0
n
2
2
100
: 0 ( x
- nx
) / (n-1) < 1 10
, n>1
n-1
стор. 47
VI. ДОПУСТИМІ ЗНАЧЕННЯ АРГУМЕНТУ
ФУНКЦІЙ
Функції Допустимі значення аргументу функцій
10
Градуси (D): |х| < 1 X 10
deg
10
Радіани (R): |х| < /180 X 10
10
sin x,
Гради (G): |х| < 10/9 X 10
cos x,
Але не для tan x:
tan x
Градуси (D): |х|
90 (2n + 1)
Радіаны (R): |х|
/2 (2n + 1)
Гради (G): |х|
100 (2n + 1) (де n – ціле число)
-1
sin
x,
-1
-1
х 1
cos
x
-1
100
tan
x|х| < 1 10
sinh x
cosh x
– 230.2585092
х 230.2585092
tanh x
-1
100
sinh
x|х| < 1 10
-1
100
cosh
x1 х < 1 10
-1
tanh
x|х| < 1
log x
-99
100
1
10
х < 1 X 10
ln x
100
10x – 1 10
< х < 100
x
100
e
– 1 10
< х 230.2585092
100
y > 0: – 1 10
< x log y < 100
100
x
y = 0: 0 < < 1 X 10
y
100
y < 0: –1 10
< x log |y| < 100
(x – ціле число, або 1/х – непарне число)
x
U
стор. 46
100
y > 0: –1 X 10
< 1/x logy < 100 (x 0)
100
y = 0: 0 < x < 1 X 10
y
100
y < 0: –1 10
< 1/x log |y| < 100
(x – ціле число, або 1/х – непарне число)
100
x
0
x < 1 10
3
100
x
|x| < 1 10
2
50
x
|x| < 1 10
100
1/x |x| < 1 10
(x 0)
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
I. MAIN FEATURES
Basic Calculations
– Negative, exponent calculations and arithmetic operations (+, -, ,
) with nesting of parenthesis at six levels.
Scientifi c Function Calculations
– Trigonometric/inverse trigonometric functions
– Hyperbolic/inverse hyperbolic functions
– Common/natural logarithm
– Square, square root, cubic root
– Power of nth and root of nth
– Factorial, permutation, combination
– Reciprocal, percentage
Memory Function and Calculations
– 1 independent memory, 27 variable memories and 1 result
memory
– Memory function in scientifi c calculations
«Base-N» Calculations
– Binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal conversions
– Basic arithmetic operations
– Logical operations (AND, OR, NOT, XOR, XNOR)
Statistical Calculations
– Mean, sum of squares, sum and number of data
– Population standard/sample standard deviation
Fraction Calculations
– Basic arithmetic operations with fractions
– Fraction /decimal number conversion
– Improper/reducer fraction conversion
E
Scientifi c Constants
– Built-in scientifi c constants are as follows:
* c (Velocity of light)
* h (Plank’s constant)
* G (Gravitational constant)
* e (Electronic charge)
* me (Electronic rest mass)
* u (Atomic mass)
p. 5
* Na (Avogadro constant)
* k (Boltzmann constant)
* Vm (Molar volume of ideal gas at s. t. p)
* g (Gravity acceleration of free fall)
Conversion between Angle Units: Degree, Radian and Grad
Hexadecimal and Decimal Conversion with Fancy Display
Format
Rectangular/Polar Coordinates Conversion
Specifying the Number of Decimal Places, the Number of Signifi -
cant Digits and Engineering Symbol Display
Random Numbers between 0.000 and 0.999
Formula Calculations
– Built-in 38 formulas
– Allows users’ input of formulas
II. DISPLAY
1. Two-tier Display
This calculator features a two-tier display. Upper tier is a 5 × 5 dot
display for displaying up to 14 characters. The lower tier composes
of 7-portions display 10 digits for a mantissa, as well as 2 digits for an
exponent. The formula is shown on the upper display and the result
on the lower display. This allows both the formula and the result to be
displayed simultaneously.
Выражение
Formula
Example: 5×8=40
5*8
40.
E
Результат вычислений
Result of calculation
2. Display Symbols
p. 6
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
5) Проведення обчислень
Приклад. Обчислити площу трикутника, якщо:
а) В = 2, С = 3, A = 2
b) B = 5, C = 3, A = 2
Відображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
Введення формули (1/2)
(1/2) ВС Sin A_ [D]
[FMLA]
ВС sin A на дисплей
FMLA
B?
Початок обчислення [CALC]
0.
[D] FMLA
C?
Введення значення
2 [EXE]
0.
змінної «В» (2)
[D] FMLA
A?
Введення значення
3 [EXE]
0.
змінної «С» (3)
[D] FMLA
(1/2) ВС Sin A_
Введення значення
2 [EXE]
1.046984901-01 [D]
змінної «А» (2)
FMLA
В?
Початок обчислень [CALC]
2.
[D] FMLA
С?
Введення значення
5 [EXE]
3.
змінної «В» (5)
[D] FMLA
A?
Значення змінної «С»
2.
[EXE]
не замінювати (3)
[D] FMLA
U
(1/2) ВС Sin A_ 2.6174-
Значення
змінної «А»
[EXE]
62253-01
не замінюв
а
ти (2)
[D] FMLA
стор. 45
Mm
34. Закон всесвітнього тяжіння:
GF
2
r
Q
35. Напруженість електричного поля:
E
2
SH
r4
36. Рівняння маси та енергії:
2
mcE
37. Коефіціент заломлення:
rsin
38. Критичний кут падіння:
2) Пошук формул:
a. Для послідовного перегляду усіх формул натисніть кнопку
[FMLA].
б. Для повернення до попередньої формули натисніть послідовно
кнопки [SHIFT] та [→].
в. Для швидкого виведення формули на дисплей введіть з
клавіатури її номер (див. вищ
е), а по
тім натисніть кнопку [FMLA]
або кнопки [→] [→].
Приклад.
7 [FMLA]
3) Введення формул до пам’яті калькулятора
Для введення формули у верхній рядок дисплею до пам’яті каль-
кулятора натисніть послідовно кнопки [SHIFT] [IN].
Приклад. Ввести формулу А
2
+ В
2
до пам’яті калькулятора:
2
2
[ALPHA] [A] [X
] + [ALPHA] [B] [X
]
[SHIFT] [IN]
Примітка. Поява на місці формули курсору, що блимає «_»
вказує на завершення процедури введення формули у пам’ять
калькулятора.
4) Видалення формул з пам’яті каллькулятора
Якщо введені формули більш не використовуються, їх можна
U
видалити з пам’яті калькулятора. Для цього натисніть послідовно
кнопки [SHIFT] та [FDEL].
Примітка. Формули, що закладені у пам’ять калькулятора за
замовчуванням, видаленню не підлягають.
стор. 44
i
s
i
n
E
1
4
)1n2n(sin
4Sr
4Sr
2
2
D FMLA
D FMLA
А
2
+ В
2
–
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
The display window features symbols that light to indicate the present
operational status of the calculator.
[S] Indicates [SHIFT] key has been pressed.
[A] Indicates [ALPHA] key has been pressed.
[H] Indicates [HYP] key has been pressed.
MODE Indicates [MODE] key has been pressed.
SD Indicates statistical calculations mode has been specifi ed.
M Indicates input data has been stored into memory (MR).
Indicates angular unit as «Degrees».
Indicates angular unit as «Radians».
Indicates angular unit us «Grads».
BUSY Indicates calculation is being executed.
FMLA Indicates formula calculation is being executed.
FRAC Indicates fraction calculation has been specifi ed.
FIX Indicates number of decimal places has been specifi ed.
SCI Indicates number of signifi cant digits has been specifi ed.
ENG Indicates engineering symbol display has been specifi ed.
mm
E
p. 7
mm
m
oo
oo
o
D
R
G
Indicates number of characters exceeds limitation of screen.
Non-displayed character can he viewed by «scrolling» right or left, as
indicated by arrows.
3. Exponential Display
During normal calculation this unit is capable of displaying up to 10
digits. However if calculation results exceed this limit, they are automati-
cally displayed in exponential format.
III. OPERATION CONTROL
All keys can perform several different functions.
For example: the key shown below can perform 4 functions:
-1
sin
A
-1
[sin] – 1) sin; 2) sin
; 3) A; 4) A
16
The function of this key differs depending on the operational mode of
calculator. If pressed directly, it performs the «sin» function. If your press
-1
the [SHIFT] key and then press [sin] key, it carries out «sin
» function. If
you press the [ALPHA] key and then press [sin] key, you can input the
variable «A». In «Base – N», «HEX» mode you can input the hexadecimal
«A» after press [sin].
Key Notation
[OFF] – Power off key.
● When the Power is turned off, mode setting and memory contents
are not lost.
Note: Auto power-off function:
If any key is not pressed in approximately 6 minutes, the auto power-off
function automatically turns off the power.
MC SC
[ON/C] – Power on/all clear/independent memory clear/standard
memory clear key.
● Press [ON/C] to turn the calculator on.
● Press [ON/C] to clear all input characters and «ERROR» message
on the display.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [ON/C] to clear all contents in independent
memory (MR).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [ON/C] to clear all contents of statistical
memory.
[SHIFT] Shift key.
● Press [SHIFT] to use upper left functions marked in yellow or red.
[ALPHA] – Alphabet key.
● Press [ALPHA] to use upper right functions marked in blue or grey.
[HYP] – Hyperbola Key.
● After pressing [HYP] and then [sin] ([cos] or [tan]) calculate the
E
hyperbolic function for the following value.
-1
-1
-1
● After pressing [SHIFT] and then [HYP] press [sin
] ([cos
] or [tan
])
to calculate inverse hyperbolic function for the following value.
[MODE] – Mode key
● Press [MODE] and then [0], [1], [2] or [3] to specify the mode of
the calculator.
[►] – Cursor shift right key
● Press [►] to move the cursor to right on the display holding it down
will cause continuous movement of the cursor in the right direction.
p. 8
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
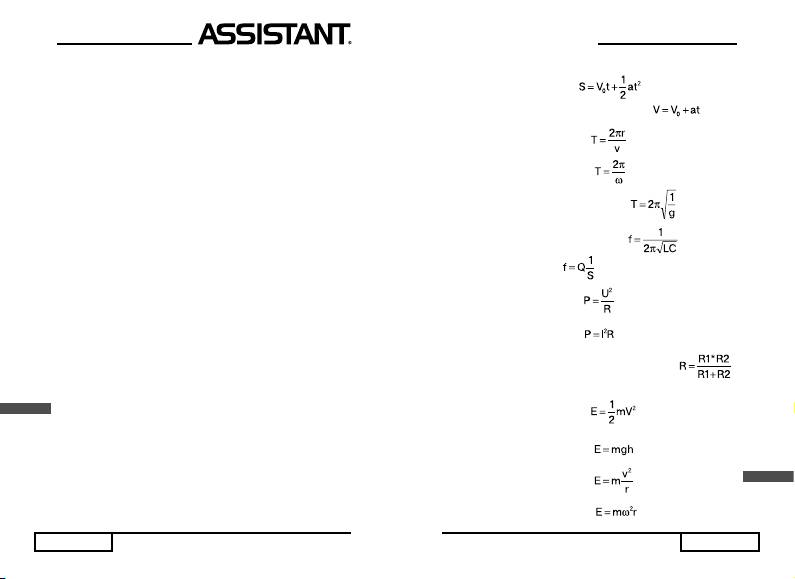
20. Відстань під час поступального руху:
21. Швидкість під час поступального руху:
22. Період руху по колу (1):
23. Період руху по колу (2):
24. Період математичного маятнику:
25. Частота електричних коливань:
26. Опір провідника:
27. Закон Джоуля – Ленца:
28. Закон Джоуля – Ленца:
29. Опір двох провідників, які з’єднані паралельно:
30. Кінетична енергія:
31. Потенційна енергія:
32. Відцентрова сила (1):
U
33. Відцентров
а сила (2):
стор. 43
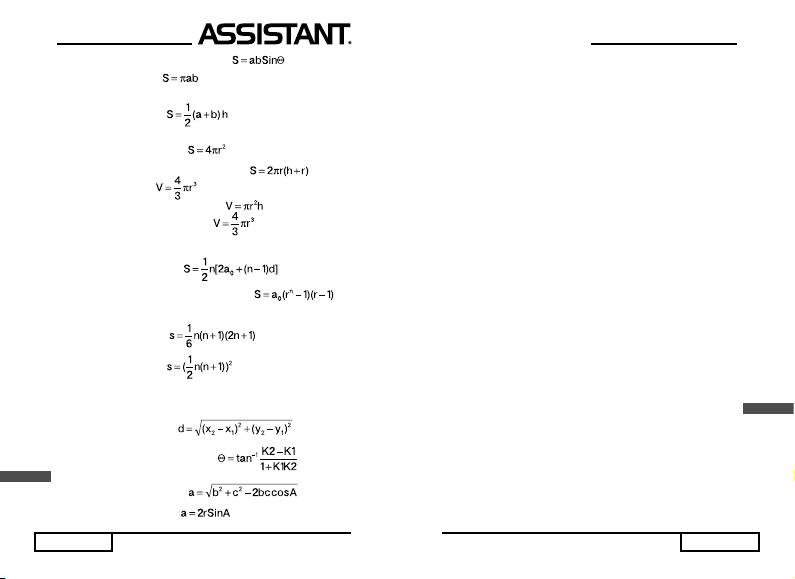
4. Площа паралелограму:
5. Площа еліпсу:
6. Площа трапеції:
7. Площа поверхні кулі:
8. Площа поверхні колового циліндру:
9. Об’єм кулі:
10. Об’єм колового циліндру:
11. Об’єм колового конусу:
12. Сума арифметичної прогресії:
13. Сума геометричної прогресії:
14. Сума квадратів:
15. Сума кубів:
16. Відстань між двома точками:
17. Кут перетину двох прямих:
U
18. Теорема косинусів:
19. Т
еорема
синусів:
стор. 42
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
[◄] Cursor shift left key
● Press [◄] to move the cursor to left on the display holding it down will
cause continuous movement of the cursor in the left direction.
FDEL me
[DEL] – Character delete/formula delete/constant me key.
● Press [DEL] to delete characters or characters string under the
cursor.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [DEL] to delete the formula displayed.
● Press [ALFHA] and then [DEL] to get constant me (electronic
rest mass).
INS u
[BS] – Delete insert, constant u key.
● Press [BS] to delete character or character string to left of cursor
when cursor is to the right of the last input character.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [BS] key to display the insert cursor «[ ]»
entering a value will be displayed in the position immediately preceding
the insert cursor location.
● Press [ALFHA] and then [BS] key to get constant u (atomic
mass).
DRG→k
[DRG] – Degrees, radians, grads selection & conversion key/con-
stant k key
● Change the unit of angle by pressing [DRG] once the changing
sequence is DEG→RAD→GRAD→DEG and the display will follow
the unit.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [DRG] to convert the unit of angle.
● Press [ALFHA] and then [DRG] lo get constant k (Boltzmann
E
constant).
BLOCK Vm
[DHBO]
– Decimal, hexadecimal, binary octal selection & conver-
sion key/
Vm key.
● Press [DHBO] to change the number system in «Base-N» mode the
changing. Sequence is DEC→HEX→BIN→OCT→DEC
● After entering a formula, press [EXE] and then [DHBO] to convert
the calculation result according to the sequence as above.
p. 9
● There are 8 digits in one block in the «Base-N» mode. Press [SHIFT]
and then [DHBO] to display the blocks one by one.
● Press [ALFHA] and then [DHBO] to get constant Vm (molar volume
of ideal gas at s. t. p.)
NORM g
[FIX] – Specifying the number of decimal places key/constant g key
● Press [FIX] and then a numeric key. The «FIX» indicator appears
and the calculation result is displayed with the number of places
specifi ed.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [FIX] to cancel «FIX», «SCI» and «ENG»
specifi cations and restore fl oating point system.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [FIX] to get constant g (gravity accelera-
tion of free fall).
ENG Na
[SCI] – Specifying the number of signifi cant digits/engineering symbol
system Na key
● Press [SCI] and then a numeric key. The «SCI» indicator appears and
the calculation result is displayed with the number signifi cant digits.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [SCI], the «ENG» indicator appears on the
display and the exponent is set to multiples of 3 for display.
● Press [ALFHA] and then [SCI] to get constant Na (Avogadro’s
constant).
ANS %
[EXE] / [=] – Execution/result/result/percentage key
● Input formula and then press [EXE] to get calculation result.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [EXE] to recall the last calculation
E
result.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [EXE] for percentage calculation.
SS
SS
S
с
[EXP] – Exponent/pi/constant с key
● Input a mantissa and then press [EXP] to execute the exponent
23
calculation. For example: to input 5.64 × 10
, input 5.64 and then press
[EXP] and 23.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [EXP] to input the value of Pi (
SS
SS
S
).
● Press [ALFHA] and then [EXP] to get constant с (velocity of light).
p. 10
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
4) Приклади статистичних розрахунків
Зображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
Видалити увесь вміст
пам’яті статистичного
[ALPHA] [SC] Scl
режиму
Ввести такі дані:
20 [ALPHA] [:] 5 [DATA]
n = (верхній ря-
значення 20 – 5 разів
30 [ALPHA] [:] 4 [DATA]
док дисплею) 5.
значення 30 – 4 рази
40 [DATA]
n = 9. n = 10.
значення 40 – 1 раз
10 [ALPHA] [:] 6 [DATA]
n = 16.
значення 10 – 6 разів
[SHIFT] [n] [EXE]
[SHIFT] [x] [EXE]
16.20.320
Обчислити значення
[SHIFT] [
x] [EXE]
7800.
таких статистичних
2
[SHIFT] [
x
] [EXE]
9.660917831
параметрів:
[SHIFT] [
] [EXE]
9.354143467
n
[SHIFT] [
] [EXE]
n-1
2 [SHIFT] [
] [EXE]
40.
2
30 [+] 2 [SHIFT] [
x
]
15630.
[EXE]
7. Обчислення за формулами
У пам’яті калькулятора закладено 38 вбудованих формул, обчис-
лення за якими здійснюють введенням до них значень змінних. У
пам’ять калькулятора можна ввести також будь-яку іншу формулу.
1) Вбудовані формули
1. Площа трикутника:
2. Площа круга:
U
3. Площа сектора:
стор. 41
2) Видалення введених даних
Приклад 1. 20 [DATA] [30] [DATA] 40 [DATA]
Для видалення останнього введенего значення (40) натисніть
послідовно кнопки [SHIFT] та [CD].
Приклад 2. 20 [DATA] [30] [DATA] 40 [DATA]
Для видалення значення «30» введіть 30 і натисніть кнопки
[SHIFT] та [CD].
Приклад 3. 20 [DATA ] 30 [D ATA] 40 [ALPHA] [:] 2 [DATA]
Для видалення з пам’яті повторюваних даних, які вводились
останніми (40 ALPHA: 2), натисніть кнопки [SHIFT] та [CD].
Приклад 4. 20 [DATA ] 30 [ALPHA] [:] 3 [DATA] 40 [DATA]
Для видалення раніш введених повторюваних даних «30 [ALPHA]
[:] 3». введіть: 30 [ALPHA] [:] 3 [SHIFT] [CD].
3) Формули статистичного розрахунку
¦
x
Середнє значення виборки:
x
n
Сумма введених даних:
¦
21
xxxx
n
2
2
22
Сумма квадратів введених даних:
¦
1
2
xxxx
n
Стандартне відхилення
для генеральної сукупності даних:
Стандартне відхилення для виборки даних:
U
(де n – кількість введених значень)
Примітка: результати статистичних розрахунків можна використо-
вувати у інших обчисленнях.
стор. 40
анных:
22
n
1
¦
xnx
V
n
1
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
3
E
p. 11
Н
[
] – Square root/cubic root/ variable «H» Key
● Press [
] and then enter a number to obtain its square root.
● Press [SHIFT] and [
] in sequence, and then enter number to
obtain its cubic root.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [
] to input variable «H».
x
y G
y
[x
] – Power of nth/root of nth/ variable «G» key
y
● Input x, press [x
] and then enter у to calculate x to the power of y.
y
● Input x, press [SHIFT] and [x
] in sequence, and enter у to calculate
the xth root of y.
y
● Press [ALPHA] and then [x
] to input variable «G».
x
e
F
[ln] – Natural logarithm & exponent/variable «F» /hexadecimal
number «F» key.
● Press [ln] and then enter a number to obtain its natural logarithm.
● Press [SHIFT] and [ln] in sequence, then enter a number to obtain
its power of «e».
● Press [ALPHA] and [ln] to input variable «F».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to input hexadecimal number «F».
x
10
E
[log] – Common logarithm/exponent of 10/varible «E» /hexadecimal
number «E» key
● Press [log] and then enter a number to obtain its common
logarithm.
● Press [SHIFT] and [log] in sequence, then enter a number to
obtain its power of 10.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [log] to input variable «E».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to input hexadecimal number «E».
-1
sin
A
[sin] – Sine/arcsine/variable «A» /hexadecimal number «A» key
● Press [sin] and then enter a number to obtain its sine value.
● Press [SHIFT] and [sin] in sequence, and then enter a number to
obtain its arcsine value.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [sin] to input variable «A».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to input hexadecimal number «A».
-1
cos
В
[cos] – Cosine/ arc cosine/variable «B» /hexadecimal number
«В» key
● Press [cos] and then enter a number to obtain its cosine value.
● Press [SHIFT] and [cos] in sequence, and then enter a number to
obtain its arc cosine value.
● Press [ALPHA] and then tan to input variable «В».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to input hexadecimal number «В».
-1
tan
С
[tan] – Tangent/arctangent/variable «C» /hexadecimal number
«С» Key
● Press [tan] and then enter a number to obtain its tangent value.
● Press [SHIFT] and [tan] in sequence, and then enter a number to
obtain its arctangent value.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [tan] to input variable «C».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to input hexadecimal number «C».
→DEG D
[D°M’S] – Decimal-Hexadecimal conversion/variable «D» /hexadeci-
mal number «D» key
● Press to enter hexadecimal value.
Example: 25°56’24» →25 [D°M’S] 56 [D°M’S] 24 [D°M’S]
● Press [SHIFT] and then [D°M’S] to convert a decimal based value
to degrees/minutes/seconds.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [D°M’S] to input variable «D».
● In «HEX» mode, press this key to enter hexadecimal number «D».
d/c h
E
b/c
[a
] – Fractions/constant h key
● Press to input fractions and mix numbers.
Example: 12/27 > 12 [a
b/c
] 27
5 3/4 > 5 [a
b/c
] 3 [a
b/c
] 4
● Input formula and press [EXE], if the calculation result is in fraction,
b/c
press [a
] to convert between fraction and decimal.
● Input formula and press [EXE], if the calculation result is in mix num-
b/c
ber, press [SHIFT] [a
] to convert between fraction and mix number.
p. 12
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
7) Логічні операції
Зображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
[DHBO] → «d»
d
20
AND5
4
10
10
20 [SHIFT] [AND] 5 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «H»
H
AB
OR23
000000Ab
16
16
AB [SHIFT] [OR] 23 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «O»
10
223
XOR6
00000225
8
8
223 [SHIFT] [XOR] 6 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «b»
1b
110
XNOR1111
11110110
2
2
110 [SHIFT] [XNOR] 1111 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «O»
10
NOT34
77777743
8
[SHIFT] [NOT] 34 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «d»
d
NEG5
-5
10
[SHIFT] [NEG] 5 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «H»
H
2B
AND5
OR4
2B [SHIFT] [AND] 5 [SHIFT]
00000005
16
16
16
[OR] 4 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «O»
10
NEG6
XOR12
[SHIFT] [NEG] 6 [SHIFT] [XOR]
77777760
8
8
12 [EXE]
6. Статистичні розрахунки
1) Введення статистичних даних
Приклад 1. Статистичні значення: 10, 50, 20
Операції, що виконуються: 10 [DATA] 50 [DATA] 20 [ DATA]
Приклад 2. Статистичні значення: 10, 30, 30, 40
Операції, що виконуються: 10 [DATA] 30 [DATA] [DATA] 40 [DATA]
● Останнє введене значення під час повторного натискання кнопки
[DATA] вводить ще раз.
Приклад 3. Статистичні значення : 20 10, 10, 10, 10, 60
Операції, що виконуються : 20 [DATA] 10 [ALPHA] [:] 4 [DATA]
60 [DATA].
U
● Для прискореного введення повторюваних даних введіть зна-
чення, натисніть послідовно кнопки [ALPHA] та [:], а потім введіть
цифру кількості повтору даних.
стор. 39
5) Взаємні перетворення двійкових, вісімкових, десяткових
та шістнадцяткових чисел
Для перетворення результату на дисплеї з одної системи числення
в іншу натискайте кнопку [DHBO] потрібну кількість разів до появи
на дисплеї позначення відповідної системи. При цьому відбувається
змінення активованої системи числення.
Зображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
Визначити, як число
[DHBO] → «d»
d
22
22
буде зображене у
22 [EXE]
10
H
00000016
двійковій,вісімковій та
[DHBO]
1b
00010110
шістнадцятковій системах
[DHBO]
10
00000026
числення
[DHBO]
6) Арифметичні операції з двійковими, вісімковими,
десятковими та шістнадцятковими числами
Зображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
[DHBO] → «b»
b
0011
+ 11010
000111011
2
2
0011 [+] 11010 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «H»
H
4B3
- AC
00000407
16
16
4B3 [-] AC [EXE]
[DHBO] → «O»
10
123
16
00002212
8
8
123 [
] 16 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «d»
d
10
/2
5
10
10
10 [] 2 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «O»
10
12
+ 5
2
00000024
8
8
8
12 [+] 5 [] 2 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «H»
H
(-2)
3 + 5
FFFFFFFF
U
16
16
[(-)] 2 [
] 3 [+] 5 [EXE]
[DHBO] → «d»
d
(2 + 5)
9
63
10
10
[(] 2 [+] 5 [)] [ ] 9 [EXE]
стор. 38
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
b/c
● Press [ALPHA] and then [a
] to input constant h (Plank’s
constant).
RANDOM
44
44
4
[(-)] – Negative/random/variable «
4
44
44
» key
● Press [(-)] and then enter a number to obtain its negative value.
● Press [SHIFT] and number between 0.000-0.999 and then [(-)] to
generate random.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [(-)] to input variable «
4
44
44
».
→ xy:
[.] – Decimal point/coordinate conversion/colon key
● Press [.] to input decimal point
● Press [SHIFT] and then [.] to convert polar coordinate (r,
44
44
4
) to
rectangular coordinate (x, y).
● Press [ALPHA] and [.] in sequence to input colon, and then enter a
number that indicates the value in the left of colon should repeat times.
NEG O
[(] – Open parenthesis/logic negative/variable «O» Key
● Press [(] to input open parenthesis.
● In «Base-N» mode press [SHIFT] and [(] in sequence, and then enter
a number, to execute «NEG» function of logic operations.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [(] to input variable «O».
NOT P
[)] – Closed parenthesis/logic not/variable «P» key
● Press [)] to input closed parenthesis
● In «Base-N» mode, press [SHIFT] and [)] in sequence, and then enter
a number to execute «NOT» function of logic operations.
E
● Press [ALPHA] and then [)] to input variable «P».
→ r
44
44
4
,
[0] – Numeric 0/coordinale conversion/comma key
● Press [0] to input numeric 0.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [0] to convert rectangular coordinate (x, y)
to polar coordinate (r,
44
44
4
).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [0] to enter comma that used to separate
two numbers.
p. 13
nCr V
[1] – Numeric 1/ combination/variable «V» key.
● Press [1] to enter 1.
● Enter n, and then press [SHIFT] and [1] in sequence, and then input
r for its combination calculation.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [1] to enter variable «V».
V
E
p. 14
V
V
V
V
W
n
[2] – Numeric 2/popuIation standard deviation/variable «W» key
● Press [2] to enter 2.
● In «SD» mode, press [SHIFT] and then [2] to calculate statistical
data of population standard deviation (
V
V
V
V
V
).
n
● Press [ALPHA] and then [2] to enter variable «W».
V
V
V
V
V
X
n-1
[3] – Numeric 3/sample standard deviation/variable «X» key.
● Press [3] to enter 3.
● In «SD» mode, press [SHIFT] and then [3] to calculate statistical
data of sample standard deviation (
V
V
V
V
V
)
n-1
● Press [ALPHA] and then [3] to enter variable «X».
nPr Q
[4] – Numeric 4/pemiutation/variabIe «Q» key
● Press [4] to input 4
● Input n, and then press [SHIFT] and [4] in sequence, and then input
r for its permutation calculation (nPr).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [4] to enter variable «Q».
¦
¦
¦
¦
¦
х R
[5] – Numeric 5/х/variable «R» key
● Press [5] to input 5.
● In «SD» mode, press [SHIFT] and then [5] to obtain sum of
statistical data (
¦
¦
¦
¦
¦
х).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [5] to enter variable «R».
¦
¦
¦
¦
¦
2
х
S
[6] – Numeric 6/
¦
¦
¦
¦
¦
2
х
/ variable «S»
● Press [6] to enter 6.
● In «SD» mode press [SHIFT] and then [6] to obtain sum of square
of statistical data (
¦
¦
¦
¦
¦
2
х
).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [6] to enter variable «S».
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
У вісімковій системі числення:
Блок 2 Блок 1
012 34567012
3 розряди 8 розрядів
11 розрядів
● У двійковій системі числення одразу після виконання обчис-
лення на дисплеї з’являється Блок 1. Послідовним натисканням
кнопок [SHIFT] та [BLOCK] на дисплей можна по черзі виводити
інші блоки. Номер блоку відображається у кінці нижнього рядка
дисплею (знаки порядку).
Приклад.
[SHIFT] 100001100011 Блок 1
[BLOCK] 011000111b
[SHIFT] 100001100011 Блок 2
[BLOCK] 000010002b
[SHIFT] 100001100011 Блок 3
[BLOCK] 000000003b
[SHIFT] 100001100011 Блок 4
[BLOCK] 000000004b
[SHIFT] 000001100011
[BLOCK] 011000111b Повернення до блоку 1
● У вісімковій системі числення одразу після виконання обчислення
на дисплеї з’являється Блок 1. Послідовним натисканням кнопок
[SHIFT] та [BLOCK] на дисплей можна по черзі виводити блоки 2
та 1. Номер блоку відображається у кінці нижнього р
ядку дисплею
(
знаки порядку).
Приклад.
[SHIFT] 12345670123 Блок 1
[BLOCK] 456701231b
[SHIFT] 12345670123 Блок 2
U
[BLOCK] 1232b
[SHIFT] 12345670123 Повернення до блоку 1
[BLOCK] 456701231b
стор. 37
3) Граничні значення обчислень
Система числення Граничні значення
Двійкова
Для додатних чисел:
01111111111111111111111111111111 Х
0
Для від’ємних чисел:
10000000000000000000000000000000 Х
11111111111111111111111111111111
Вісімкова
Для додатних чисел:
17777777777
Х 0
Для від’ємних чисел:
20000000000
Х 37777777777
Десяткова
Для додатних чисел:
2147483647
Х 0
Для від’ємних чисел:
-1 Х
-2147483648
Шістнадцяткова
Для додатних чисел:
7FFFFFFF
Х 0
Для від’ємних чисел:
FFFFFFFF
Х 80000000
4) Блоки у двійковій та вісімковій системах числення
У двійковій та вісімковій системах числення калькулятор пере-
творює числа у блочну форму. Найбільша кількість відображуваних
розрядів у двійковій системі (32 розряди ) розбивається на 4 блоки
по 8 розрядів у блоці. Найбільша кількість відображуваних розрядів у
вісімковій системі (11 розрядів ) розбивається на 1 блок з
8 розрядів та о
дин
блок з трьох розрядів.
Приклад. У двіковій системі числення:
Блок 4 Блок 3 Блок 2 Блок 1
U
10000111 01100101 01000011 00100001
8 розрядів 8 розрядів 8 розрядів 8 розрядів
32 розряди
стор. 36
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
n! L
[7] – Numeric 7/factorial/variable «L» key.
● Press [7] to enter 7.
● Enter n, and then press [SHIFT] and [7] in sequence for its factorial
calculation (n!).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [7] to enter variable «L».
n M
[8] – Numeric 8/Statistical data number/Variable «M» key
● Press [8] to enter 8.
● In «SD» mode press [SHIFT] and then [8] to obtain the number
of statistical data (n).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [8] to enter variable «M».
x
N
[9] – Numeric 9/x/variable «N» key
● Press [9] to input 9.
● In «SD» mode press [SHIFT] and then [9] to obtain mean of
statistical data (
x
).
● Press [ALPHA] and then [9] to input variable «N».
OR Y AND T XOR U XNOR Z
[+] ; [] ; [
]; [–] – Arithmetic/logic operations key
● Press [+] ; [
] ; []; [–] to carry out addition, multiplication, division
and subtraction, from left to right.
● Press [SHIFT] and then these keys to carry out «OR», «XOR»,
«AND», «XNOR» of logical operation.
● Press [ALPHA] and then these keys to enter variable «Y», «T»,
E
«U», «Z».
RCL J
[STO] – Variable memory/recall memory /variable «J» key
● Press [STO] and then enter an alphabet character to store the
displayed value into the alphabet variable memories.
● Press [SHIFT] and [STO] in sequence, and then input an alphabet
character to display the value stored.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [STO] to enter variable «J».
p. 15
CD К
[DATA] – Statistical data input/statistical data clear/variable «К» key
● In «SD» mode press [DATA] to enter statistical data.
● In «SD» mode press [SHIFT] and [DATA] to clear the data stored
in memory.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [DATA] to enter variable «K».
M – MR
[M+] – Memory plus/memory minus/memory recall key.
● Press [M+] to add entered the value to independent memory
(MR).
● Press [SHIFT] and then [M+] to subtract the entered value from
independent memory.
● Press [ALPHA] and then [M+] to display value in independent
memory (MR).
← G
[FMLA] – Sequential search/counter-sequence search/constant
G key
● Press [FMLA] to recall formula stored into memory in sequence.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [FMLA] to return to previous formula ap-
peared on the display.
● Press [ALPHA] and [FMLA] to get constant G (gravitational
constant).
IN e
[CALC] – Formula calculation/formula store/constant e key.
● Press [CALC] to execute the recalled formula.
● Press [SHIFT] and then [CALC] to store the displayed formula
in then memory.
E
● Press [ALPHA] and then [CALC] to get constant e (electronic
charge).
IV. BEFORE USING THE CALCULATOR
1. Mode Selection
[MODE] [0]: Scientifi c calculation
p. 16
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
● Якщо загальна кількість символів дробу, включно із її цілою
частиною, числівником, знаменником чи розділовими знаками,
перевищують 10, результат у рядку виводу відображається у вигляді
десяткового числа з плаваючою комою.
5. Операції у режимі подання чисел за основою «n»
● У режимі подання чисел за основою «n» виконуються об-
числення у двійковій, вісімковій, десятковій та шістнадцятковій
системах числення.
● Установка та зміна системи числення у режимі подання чисел
за основою «n» здійснюється за допомогою кнопки [DHBO]. По-
слідовність зміни систем числення є такою: десяткова (DEC) →
шістнадцяткова (HEX) → двійкова (BIN) → вісімкова (OCT). Під час
у
ст
ановки цих систем числення на дисплеї з’являються відповідні
символи : «d» «H». «b». «o».
1) Цифри систем числення калькулятора
Система числення Цифри, що використовуються
Двійкова (BIN) 0,1
Вісімкова (OCT) 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
Десяткова (DEC) 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Шістнадцяткова (HEX) 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, A,B,C,D,E,F
● У режимі подання чисел за основою n можна вводити цифри
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9, A,B,C,D,E,F. Проте, якщо цифри, що вводяться,
не використовуються у поточній системі числення, під час виводу
результатів обчислень на дисплеї з’явиться повідомлення про по-
милк
у «SynERROR».
2) Кількість відображув
аних розрядів результату для кожної
системи числення
Система числення Число відображуваних розрядів
Двійкова До 32 розрядів
(4 блоки по 8 розрядів)
Вісімкова До 11 розрядів
(1 блок з восьми розрядів
U
та 1 блок з трьох)
Десяткова До 10 розрядів
Шістнадцяткова До 8 розрядів
стор. 35
Відображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
Вивести на дисплей зна-
[ALPHA] [c] [EXE] 299792458.
чення швидкості світла
[ALPHA] [c] [/] 2 [+]
C/2 + 3
149896232.
3 [EXE]
Вивести на дисплей
-11
значення гравітаційної
[ALPHA] [G] [EXE] 6.672
постійни G
[ln] 5 [ALPHA] [Na]
ln5Nа
56.36432195
[EXE]
4. Операції з дробами
● Дроби вводяться та відображаються на дисплеї у такому порядку:
ціла частина, числівник та знаменник.
● Дроби можуть вводитись тільки у режимі операцій з дробами
«FRAC». Десяткові дроби і порядок у цьому режимі вводитись
не можуть.
Відображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
2
3
b/c
b/c
2 [a
] 3 [+] 1 [a
] 3
1
b/c
2
5 12
3
4
[a
] 4 [EXE]
56
8
b/c
b/c
56 [a
] 13 [/] 8 [a
]
/
5
5 13
13
10
10 [EXE]
128
2 [ab/c] 128 [/] 564
2
2
32 41
564
[EXE]
1
1 [/] [(] 1 [ab/c] 2 [+] 1
1
1
1 3
7
[ab/c] 5 [)] [EXE]
2
5
7
2 u
2 [] 7 [ab/c] 12 [EXE] 1
3 6
12
2 [ ] [(] 2 [-] 2 [ab/c] 3
2
2 3
[)] [EXE]
2
U
2.666666667
2(2 u
)
[ab/c]
3
2
2 3
[ab/c]
8
3
[SHIFT] [d/c]
2 2
3
[SHIFT] [d/c]
стор. 34
...YOUR ASSISTANTS
[MODE] [1]: «Base-N» mode
● For binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal calculations, conversion
and logical operations.
[MODE] [2]: «SD» mode
● For standard deviation calculation (when the mode is selected, «SD»
will be shown on the display).
[MODE] [3]: «FRAC» mode
● For fraction calculation (when the mode is selected, «FRAC» will
be shown on the display).
2. Angle Unit Defi nition
● Press [DRG] key once to change angle unit, the changing sequence
is DEG→RAD→GRAD→DEC, the angle unit is displayed as «D», «R»,
«G» respectively.
3. Number Display System Defi nition
There are three number display systems besides fl oating point system
regarded as default display system:
1) «FIX» Mode
● Press [FIX] and then numeric keys (0-9) to specify the number of
decimal places (the «FIX» indicator appears on the display).
2) «SCI» Mode
● Press [SCI] and then numeric keys (0-9) to specify the number of
signifi cant digits (0 indicating 10 digits) (the «SCI» indicator appears
on the display).
3) «ENG» Mode
● Press [ENG] to specify the engineering display and the exponent
E
is set to a multiple of 3 for display (the «ENG» indicator appears on
the display).
● Press [NORM] key to cancel «FIX», «SCI», «ENG» specifi cation
and return to fl oating point display system, also cancel degree/radian/
grad specifi cation.
● Even if the number of decimal places and number of signifi cant
digits are specifi ed, internal calculations are performed in 12 digits for a
mantissa, and the displayed value is stored in 10 digits.
p. 17
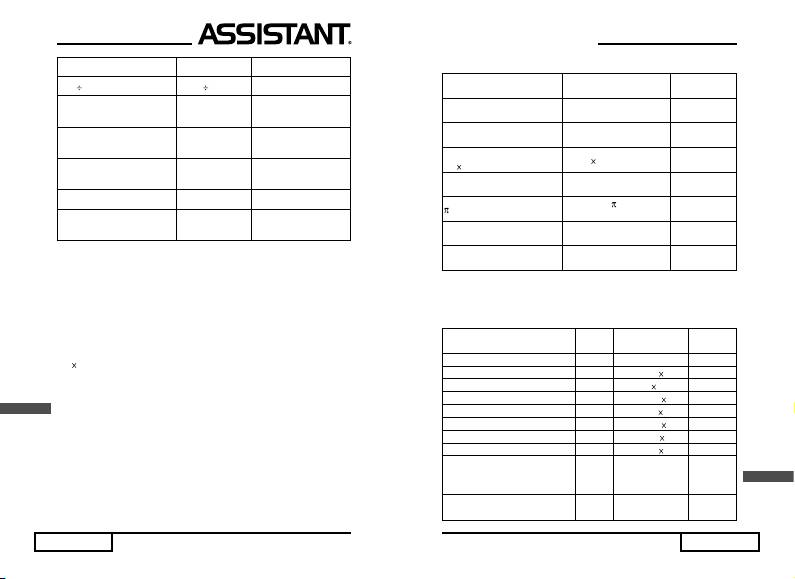
Example Operation Display (Lower
)
100 6 100 [] 6 [EXE] 16.66666667
Five decimal places
[FIX] 5 16.66667 FIX
specifi ed
Four signifi cant digits
[SCI] 4 1.667 SCI
specifi ed
Engineering display
[SHIFT] [ENG] 16.66666667 00 ENG
specifi ed
Specifi cation cancelled [SHIFT] [NORM] 16.66666667
Three decimal places
[FIX] 3 [/] 5
16.667 FIX
specifi ed: Ans / 5
[EXE]
3.333 FIX
● After specifying «FIX», «SCI», «ENG» mode, the calculation
result displayed is rounded up or down lowest digit position in the
specifi ed range.
4. Calculation Range
The allowable input/output range is l0 digits for a mantissa and 2 digits
for an exponent. Calculations are performed internally with а range of 12
digits for a mantissa and 2 digits for an exponent. Calculation ranges:
99
99
± 1 10
~ ± 9.999999999 х 10
.
5. Inputting Characters Number
E
This calculator features 100-step area for calculation execution. One
function comprises one step. Each press one key comprises one step.
-1
Though such operations as [SHIFT] [x
] require two key operations, they
actually comprise only one function and require only one step.
These steps can be confi rmed using the cursor. With each press of
the [◄] or [►] key, the cursor is moved one step. Input characters are
limited to 100 steps. Usually, the cursor is represented by a blinking «█»,
but once 100th step is reached, the cursor changes to a blinking «_» and
the character cannot be entered no longer.
p. 18
...ВАШІ ПОМІЧНИКИ
2) Збереження у пам’яті значень змінних
Відображення
Приклад Операції
на дисплеї
Зберегти число 25.6 як
25.6 [STO] [A] 25.6
змінну «А»
Вивести значення змінної
[SHIFT] [RCL] [A] 25.6
«А» на дисплей
Зберегти результат виразу
20 [] 3.5 [STO] [D] 70.
20
3.5 як змінну «D»
[ALPHA] [A] [(] 2 [+] 3
A(2 + 3)
128.
[)] [EXE]
[SHIFT] [ ] [ALPHA]
D
219.9114858
[D] [EXE]
Зберегти результат виразу
[SHIFT] [ALPHA] [A] [+]
95.6
А+D як змінну «В»
[ALPHA] [D] [STO] [B]
Вивести значення змінної
[SHIFT] [RCL] [B] 95.6
«В» на дисплей
3) Фізичні константи
У пам’ять калькулятора закладено 10 фізичних констант:
Позна-
Одиниці
Назва
Значення
че ння
виміру
Швидкість світла с 299792458 м/с
-34
Постійна Планка h 6.626176
10
Дж·с
-11
2
–2
Гравітаційна постійна G 6.672 10
Н·м
·кг
-19
Заряд електрону e 1.6021892 10
Кл
–31
Маса електрону me 9.109534 10
кг
-27
Маса атому U 1.6605655
10
кг
23
-1
Число Авоґадро NA 6.022045 10
моль
-23
.
-1
Постійна Больцмана k 1.380662 10
Дж
К
Молярний об’єм ідеального
3
.
-1
газу (за нормальних темпера-
Vm 0.02241383 м
моль
U
тури і тиску)
Прискорення вільного
.
-2
g 9.80665 м
с
падіння
стор. 33

