Xoro HSD 8420 – страница 9
Инструкция к DVD-проигрывателю Xoro HSD 8420
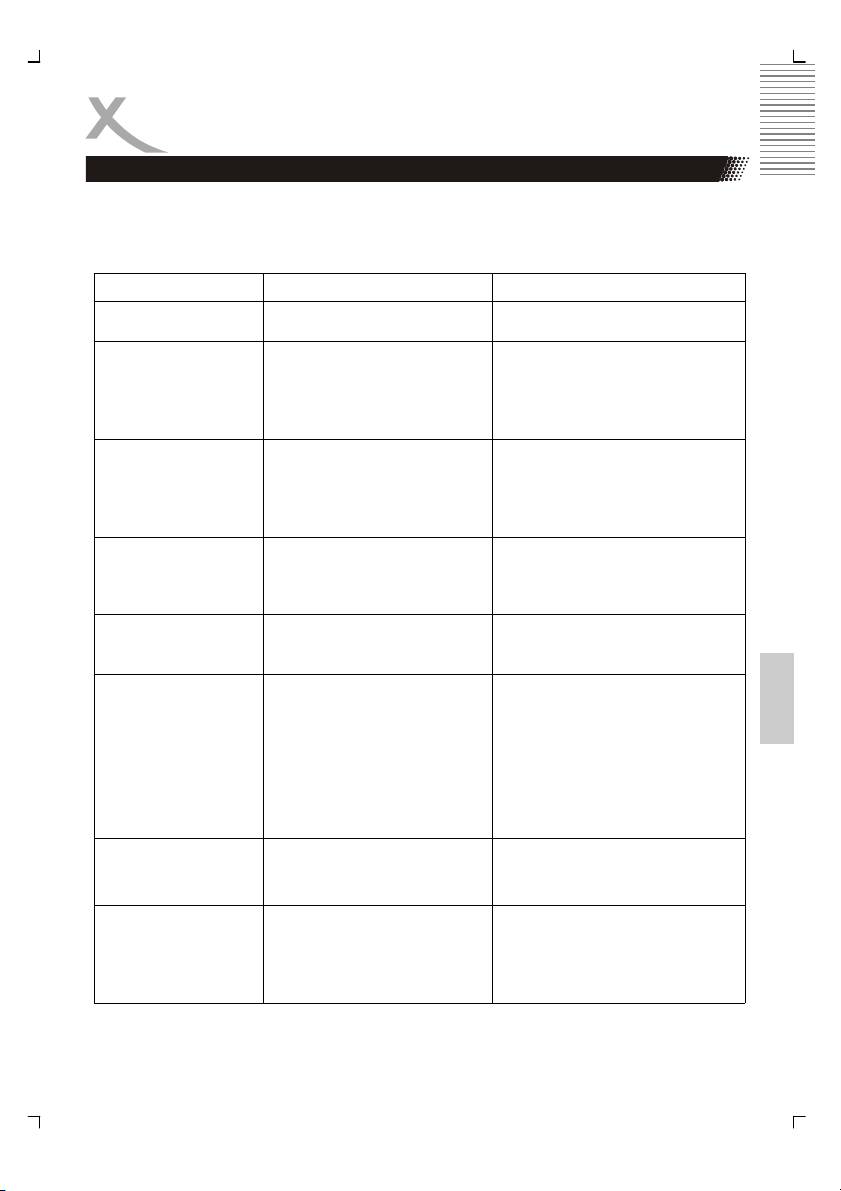
Solución de problemas
Ante cualquier dificultad al utilizar el reproductor, consulte esta guía antes de solicitar
asistaencia técnica. Soporte técnico de Xoro/MAS: Tel: 040/77 11 09 17, Internet:
www.xoro.de/support.htm
Problema
Causa Solucion
No enciende
El cable de alimentación está
Conecte el cable de alimentación
desconectado
No hay imagen
• El televisor no está configurado para
• Seleccione la salida de video del televisor
recibir señal de salida de DVD
apropiada para que la imagen del
reproductor aparezca en la pantalla del
• El cable de video no está conectado
televisor.
firmemente
• Conecte firmemente el cable del video
• El modo de video de DVD no es el
mismo del televisor
• Ver “conectar el televisor”
No se escucha el
• El cable de audio no está conectado
• Conecte el cable de audio
sonido
firmemente
• Encienda el equipo conectado con los
• El equipo está con la salida de audio
cables de audio
está apago
• Ajuste las configuraciones de audio
• El ajuste del tipo de salida de audio
correctamente
no es correcto
La imagen que se
• El disco está sucio
• Retire el disco y límpielo
reproduce en
• Esta en modo avance rápido o
• En algunas ocasiones pueden ocurrir
ocasiones se
retroceso rápido
pequeñas distorsiones en la imagen. Esto
no significa un mal funcionamiento.
distorsiona
El brillo no es estable o
• Efecto de la protección contra copias • Conecte el reproductor de DVD
se producen ruidos en
directamente al televisor
la reproducción
Español
El disco no se
• No se colocó el disco
• Inserte el disco
reproduce
• Se colocó un disco que no puede
• Verifique el tipo de disco y sistema de
reproducirse
color
• El disco esta dado vuelta
• Inserte el disco correctamente
• El disco no está colocado
• Inserte el disco en la bandeja
correctamente
correctamente
• Aparece un menú en la pantalla
• Limpie el disco
• Esta activada la función “control de
• Presione el botón SETUP para sacar el
padres”
menú de la pantalla. Cancele la función
de bloque o cámbiela.
Los botones no
Fluctuaciones en la administración
Encienda o apague el equipo o desconéctelo
eléctrica y otras anormalidades como
de la toma de alimentación y vuelva a
funcionan
electricidad estática pueden interrumpir
conectarlo.
su correcto funcionamiento
El control remoto no
• No se orienta el control remoto hacia
• Apunte el control remoto al sensor remoto
funciona
el sensor remoto del reproductor
del reproductor.
correctamente
• Hay demasiada distancia entre el
• Accione el control remoto dentro de una
control remoto y el reproductor
distancia de 7 m.
• Las pilas del control remoto están
• Cambie las pilas del control por nuevas
agotadas
29
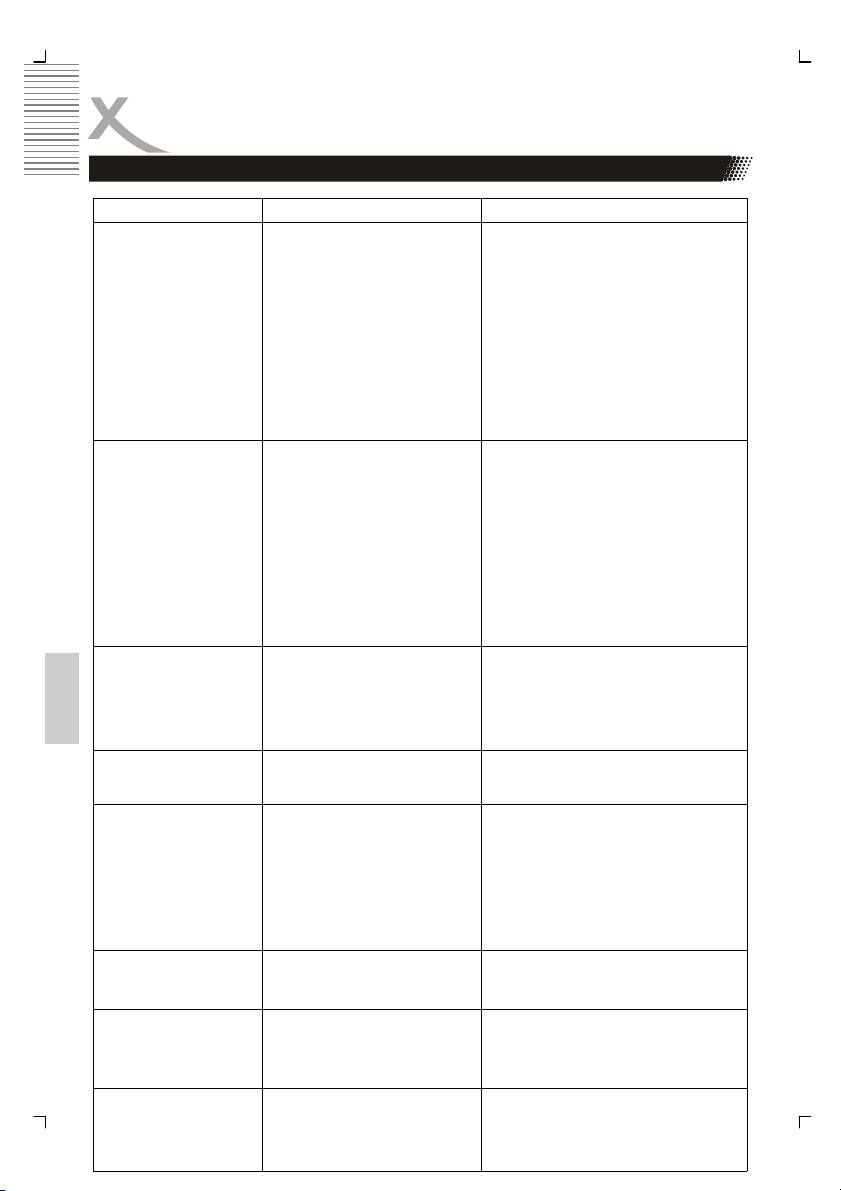
SOLUCION DE PROBLEMAS
Problema Causa Solucion
Y Pb Pr (YUV) No hay
• El cable de video no esta
• Conecte el cable de video firmemente
imagen o la imagen es
conectado firmemente
distorsionada
• Ajuste la salida de video en el modo
• El modo del reproductor no es
exploración progresiva
compatible
• Seleccione en el televisor la entrada
• El televisor no es compatible
de video adecuada de manera tal que
con la salida de del
pueda verse la imagen del
reproductor
reproductor
• El televisor puede no ser compatible
con el reproductor de DVD. Cambie a
la salida NTSC o utilice CSB,
SVIDEO o euroconector para
conectar el televisor
HDMI
• El cable de video no está
• Conecte el cable de video firmemente
NO hay imagen
conectado firmemente
• Configure la salida de video con
• El modo de video del
modo HDMI (HD)
reproductor no es compatible
con el televisor
• Elija la entrada de video adecuada en
el televisor para que pueda verse la
• La televisión no esta
imagen del reproductor.
configurada para señal de
salida de reproductor
• El televisor puede no ser compatible
con el reproductor de DVD. Cambie a
la salida NTSC o utilice CSB,
SVIDEO o euroconector para
conectar el televisor
La imagen se
• La imagen puede verse distorsionada
distorsiona durante el
• Ud presiona los botones >> o
avance/retroceso
<< durante el avance o
rápido
• Es avance o retroceso normal
retroceso rápido
Español
• Presione el botón > (Play) para
velocidad normal
No hay imagen 4:3 o
• Configuración incorrecta
• Elija la configuración correcta en la
16:9 (imagen
mediante TV TYPE
función TV TYPE que sea compatible
distorsionada)
con el televisor
Audio y/o idioma de
• No se pudo elegir el audio o
• Si el audio y/o el idioma de subtítulos
subtitulo no están
idioma de subtitulo
no se encuentra disponible en el
configurados
disco, el idioma seleccionado en la
configuración inicial no podrá
verse/oirse
• Audio alternativo (o idioma alternativo
no se selecciona con los discos que
tienen subtítulos) o idioma no puede
ser más que un idioma seleccionado
No se puede cambiar el
• Esta función depende de la
• Si un disco tiene un número de
ángulo
disponibilidad del software
ángulos grabados, estos serán solo
utilizados para determinadas
Olvido de contraseña
• Mientras la unidad está en modo de
detenimiento, ingrese al modo
SETUP y la contraseña 8888 para
desactivar la configuración de
bloqueo de padres
30
No hay repetición, no
• Algunos reproductores no
• En el modo Program playing, las
hay función A-B
tienen función aleatoria
funciones no repetición, A-B están
disponibles.
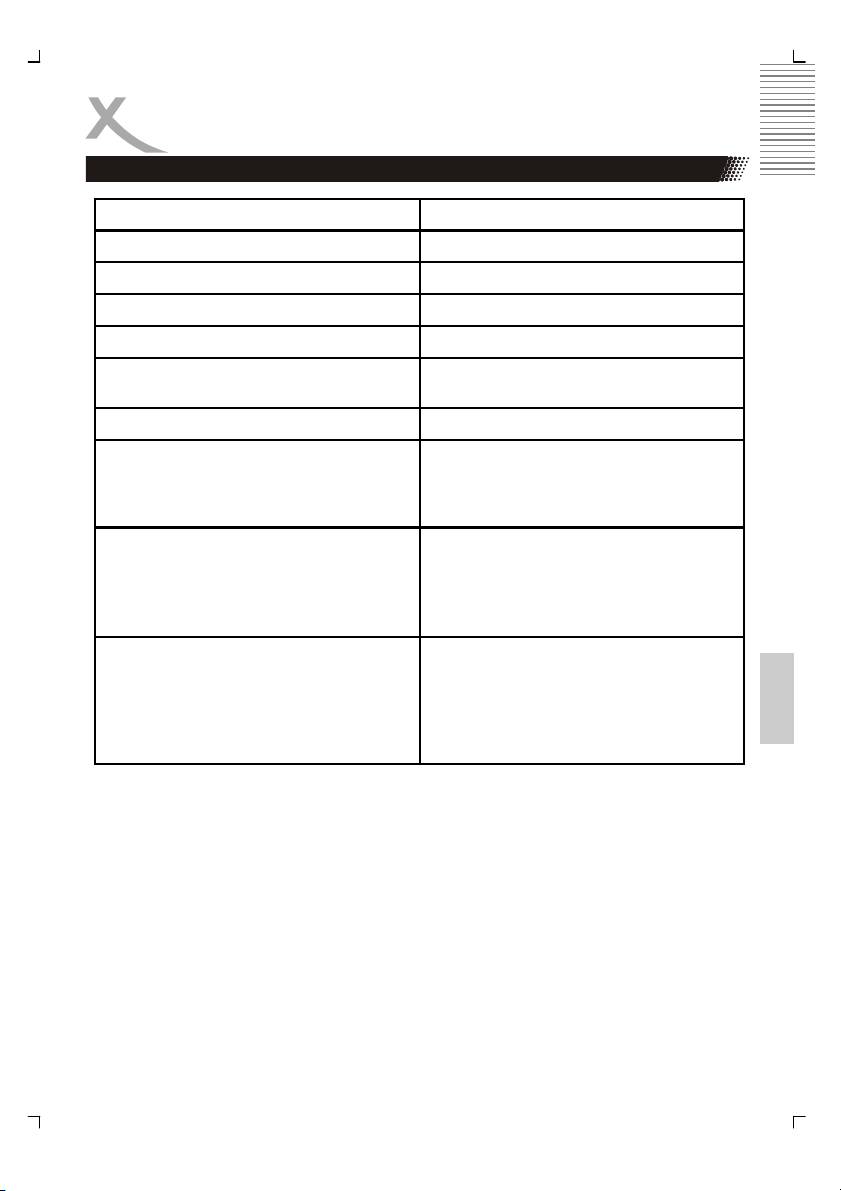
ESPECIFICACIONES
Energía eléctrica AC 181-240V 50-60Hz
Consumo de energía 20 W
Peso 2.1 kg
Tamaño 360 x 250 x 38 mm (W/H/D )
Sistema de señal PAL / NTSC / AUTO
Laser Laser semiconductor
Longitud de onda 650 nm and 780nm
Rango de frecuencia
+3dB (20Hz - 20kHz)
Funcionamiento:
Temperatura
0° - 40° Celsius
Humidad
5—90 % (sin condensación)
Estado
Horizontal
Video:
Salida de video compuesta
1.0 + 0,2Vp-p, 75 Ω
Resolución horizontal
≥ 500 líneas
Relación Señal/Audio
≥ 60 dB
DAC
14bit / 108 MHz
Audio:
Salida de audio
2.0 + 0.2 /-0.8Vrms (1kHz 0dB)
Español
Distorsión harmónica
≤ 65dB (JIS-A 1kHz, típica)
Rango dinámico
≤ 80dB (JIS-A 1kHz, tìpical)
Relación audio/ruido
≤ 90dB (JIS-A 1kHz, tipica)
DAC
24bit / 192 kHz
31

GLOSSARY
5.1
5.1-multichannel encoding means, that 5 audio channels with full frequency response are
present (left, center, right, surround left, surround right) plus a subwoofer channel
(represented by the „.1”) providing deep humming frequencies you are used to know from
®
®
modern cinemas. Both Dolby Digital
(including AC3) and DTS
support 5.1-coding and –
decoding.
Aspect ratio: 4:3 and 16:9
Full Frame refers to programs developed for TV display with an aspect ratio of 4:3.
Widescreen refers to programs developed for screens with an aspect ratio of 16:9.
If a widescreen program is displayed on a 4:3 screen, the picture will have black borders on
top and bottom.
CD
A CD (Compact Disc) is a metal-coated plastic disc. It has a diameter of 12 cm and a
thickness of anout 1,2 mm. It was developed by Sony and Philips in 1985. The advantages
are digital storage of music enabling very natural sound reproduction. Beyond this, the data
is stored more compact, the handling is easy. The long lifetime of the media and the fact that
usage does not decrease quality made the CD the ideal storage media.
In the meantime, 12 different storage media have been developed from the first CD. The
mostly used are CD-DA (Compact Disc - Digital Audio) , CD-ROM (Compact Disc - Read
Only Memory), and the DVD (Digitale Versatile Disc).
One can store about 74 to 80 minutes of music on a CD (-DA). This is equal to 650 to 700
MB. Signal transmission is performed touchless with a laser beam. The CD is being read
from the middle to the outer side. The data or music is recorded in a spiral from the middle
to the outer side.
A CD has pits and lands, the distance is about 1,6 mm. The laser light created by a laser
diode passes different mirrors and prisms and then is focused by a lens to a laser beam.
This laser beam scans the data spiral of the CD. On the pits, the laser beam is reflected in
another direction and is detected by a photocell. The photocell transmits the signal to a
microprocessor which converts the digital data to an audio signal. The rest is done by the
sound system.
Component-Signal
please refer to YUV
Contrast
Means the range of luminance between the brightest and the darkest pixel which can be
displayed.
CVBS
Composite Video Interface. The video signal is transmitted via a single signal line. CVBS
should only be used, if your playback device does not offer other interfaces for connection
with you Xoro TV set, as CVBS due to technical reasons delivers worst quality of all
available interfaces (please also refer to YUV, S-Video, SCART and RGB). The CVBS
interface can easily be identified from the yellow colour of the RCA jack.

GLOSSARY
®
Dolby Digital
5.1
®
Dolby Digital
5.1 is a system for transmission and storage of 5.1 channel sound on digital
media as DVD, digital TV and satellite transmission. Different from the codecs Dolby
®
®
Surround
and Pro Logic
who do not work with channel separation to encode the surround
®
sound in a stereo recording, Dolby Digital
is a discrete system where the different audio
channels keep completely separated during encoding and decoding. Dolby Digital 5.1 is
industry standard for coding of DVD movies with surround sound.
DSP
Digital Signal Processor. Microprocessor for digital processing of signals. Virtual Surround
for example is created with a DSP.
®
DTS
®
®
®
DTS
is a coding standard similar to Dolby Digital
. DTS Digital Surround
is a multichannel
®
surround system from Digital Theater Systems. Similar to Dolby Digital
it uses up to 5.1
channels. Different from Dolby, the data rate can be far above 1 Mbit/sec so the sound is not
®
compresses as strong as in Dolby Digital
resulting in a higher sound quality.
The frequency range is from 20Hz to 20kHz at 20Bit, but the subwoofer channels only
transmits frequencies below 80Hz. The coding system also is called CAC.
DVD
The DVD (Digital Versatile Disk) was introduced in 1995 and is a storage media with a large
capacity.
While a standard CD can store 650 MB of data, the DVD can store up to 9 GB. Especially
when it comes to video playback, a large storage capacity is important. Beyond its high
capacity, the consumer enjoys high quality video and audio. A DVD can store up to 8
different audiostreams, so in best case, the movie can be watched in 8 different languages
Photo-CD (JPEG CD)
A Photo-CD is a storage system for image storage on a CD-ROM in a platform independent
multi resolution structure (support of different resolutions and file formats, e.g. JPEG, BMP,
etc). As a single camera film dies not fill a complete CD, more films can be added to the CD
at a later time. A CD-ROM drive must be multisession enabled to load images from a Photo-
CD.
GUI
Graphic User Interface. See OSD
HDCD
Pacific Microsonics has developed a digital audio technology using the full potential of a CD.

GLOSSARY
Hosiden-connector
4-pin connector for S-Video connections.
HUE
HUE settings affect the colour balance of the picture.
Interlaced
The picture is created by writing two half pictures with a 1 line set-off on the screen. This is
standard on conventional 50 Hz TV sets.
®
Kodak Picture CD
®
The KODAK Picture CD
is the ideal media for allround photographers. All pictures are
stored at an excellent resolution of 1024 x 1536 pixel. On the KODAK Picture CD, the
images of your camera film strip are stored. It is not possible to add pictures at a later point
of time.
®
Note: There also are „Kodak Foto CDs
“ available. As they have a proprietary file format,
your DVD player cannot playback these media.
LPCM
LPCM stands for: Linear Pulse Code Modulation.
Digital, uncompressed audio recording. Standard on Audio-CDs.
MP3
MPEG 1 Layer 3 Codec, or short MP3, was developed in 1987 by Fraunhofer Institut für
Integrierte Schaltungen and was a revolution in audio compression. In 1992 it became part
of MPEG-1 video format. As MP3 offered high quality audio at incredible small file size, it
became an won standard. With this codec one can compress audio files to about 1 MB /
minute.
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a standard used primarily to compress audio and video (AV) digital data.
Introduced in late 1998, it is the designation for a group of audio and video coding standards
and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG).
The uses for the MPEG-4 standard are web (streaming media) and CD distribution,
conversation (videophone), and broadcast television, all of which benefit from compressing
the AV stream. MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other
related standards.
By MPEG-4 could be used a lot of different audio compression method. Most popular are
MP3 and AC3.
NTSC
Widespread TV standard, espacially in US and Asia. 525 (480 viewable) Lines and 60 Hz
refresh rate. Describes the way the video information (brightness, color, refresh rate etc.) is
transmitted. Within Europe, this video standard only appears on imported media (like US
DVDs).

GLOSSARY
OSD
The OSD (On Screen Display) is all the menus and options shown on the screen.
PAL
European TV standard. PAL stands for Phase Alternation Line; refresh rate: 50 Hz,
Zeilenauflösung: 625 Lines, 576 visible lines. Describes the way the video information
(brightness, colour, refresh rate etc.) is transmitted.
PBC
PBC stands for playback control. This function can be used to show a menu on Video CD’s
(if contained on the VCD). One can move in this menu with the arrow keys and select the
desired function with “enter”.
®
Pro Logic
®
Dolby Pro Logic
is a matrix decoder for decoding the four surround sound channels
®
contained in the stereo track of Dolby Surround
encoded programs (e.g. VHS movies or TV
shows). Dolby Surround is a matrix coding system mixing four channels (left, center, right,
surround) to a stereo track. A Pro Logic decoder separates these four channels during
playback. Without Pro Logic decoder, the program only has stereo sound
Progressive Scan
Progressive Scan writes a whole picture in one step, while the normal interlaced TV-picture
is composed of two half pictures. It delivers a significally enhanced picture, especially when
used on vide beamers, PC monitors or LCD TV.
RGB
Red Green Blue. Describes the way of transmission and display of video signals. The three
in TV systems used colours red, green and blue are transmitted separately. When used for
connection between playback device and TV set, it delivers a quality similar to
YUV.
S/PDIF
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a digital transmission standard for audio data.
S/PDIF can transmit audio files from one source to another without having to leave the digital
transmission which would result in worse quality.
S-Video
Describes the way video signals are transmitted. With S-Video, luminance and color
information are transmitted separately. S-Video interface can easily be identified by its 4-
ports in a round connector.
SECAM
French TV standard. It is also used outside France in some Easter European countries.
Refresh rate is the same as in PAL standard (50 Hz). The signal produces 625 TV lines.

GLOSSARY
Super Video CD (SVCD)
SVCD stands for Super Video CD. SVCD’s are very similar to VCD’s, one can store 35 – 60
minutes of high quality video with up to 2 Stereo audio tracks and 4 different subtitles. All
Xoro DVD players can play SVCD’s.
Video CD(VCD)
VCD stands for "Video Compact Disc". VCD’s are similar to normal CDs. They contain
movies with sound. A VCD can store 74 to 80 minutes of video with stereo sound. For the
storage of audio and video, MPEG-1 is used. All Xoro DVD players can play VCD’s.
YPbPr
please refer to YUV
YUV
Videosignal with separated transmission of color and brightness information. Similar to RGB,
the signal is transmitted via tree separate RCA cables. Also called Component Signal. YUV
delivers best signal quality available with analogue signal transmission.

NOTES


